Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
The opening and closing of stomata depend upon the changes in the turgidity of their guard cells. Due to the absorption of water, the guard cells become turgid. Their inner walls are pulled apart by their outer wall. The gap between the guard cells becomes wider and stomata open. When guard cells are flaccid due to loss of water, the outer walls are not stretched, their inner walls are not pulled apart decreasing the gap between the guard cells and stomata close.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between the following:
Stomata and lenticels
Choose the correct answer:
Stomata can open in night also in _______________
The apparatus shown here is Girreau’s poto-meter designed to demonstrate unequal transpiration from the two surfaces of a dorsiventral leaf. Before keeping the leaf in between the cups, anhydrous calcium chloride (CaCl2) contained in two small vials were weighed and placed in both the cups. The ends of the cups were closed with corks through which two mercury manometers were connected. After a few hours, CaCl2 vials were taken out and weighed again.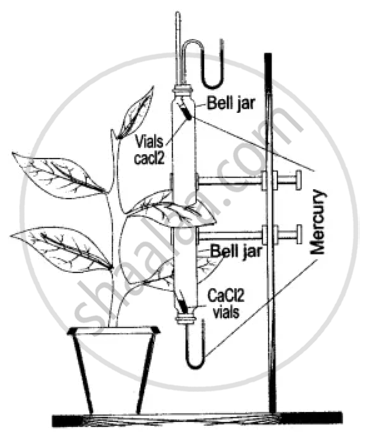
(i) What is the purpose of keeping CaCl2 vials inside the cup?
(ii) After a few hours, the CaCl2 vials were taken out and weighed again. Will you expect any difference in weight? If so, give reasons.
(iii) What was the purpose of using a mano-meter?
(iv) What do you mean by transpiration?
Name the following:
The process of getting rid of excess water in the form of water vapour through the stomata.
Name the following:
A plant having sunken stomata.
State the Location:
Stomata
State the Location:
Guard cells
Mark the most appropriate answer in the following:
Stomata open during day and close at night because:
The paper used to demonstrate unequal transpiration in a dicot leaf is ______.
The upper layer of mesophyll in a leaf consists of elongated ground tissue called ______.
