Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the construction and working of the following. Draw a neat diagram and label it.
Electric Generator (AC)
उत्तर
Electric Generator principle : An electric generator is a machine that generates electricity by rotating its rotor in a magnetic field. Thus, it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Construction: A generator consists of a rectangular coil MNST of insulated copper wire placed between two strong magnetic poles. The two ends of the coil MNST are connected with brushes A and B of rings C and D respectively. The inner sides of the rings are insulated. They are attached with an axle X, which can be rotated mechanically. Brushes A and B are connected with a galvanometer that can measure the flow of current in coil MNST.

Working: When the axle is rotated, lengths MN and ST move up and down respectively. Since lengths MN and ST are moving in a magnetic field, a current gets induced in these lengths caused by an electromagnetic induction. The direction of the induced current in both the lengths is given by Fleming’s right hand rule.

Since length MN is moving upwards in the magnetic field that acts from left to right, the direction of the induced current will be from M to N. Similarly, the direction of the induced current in length ST will be from S to T. Hence, an induced current will set up in the coil in the direction MNST, which produces deflection in the galvanometer.
After half-rotation, length MN starts moving down, whereas length ST starts moving up. The direction of the induced current in the coil gets reversed i.e., the induced current will now flow from T to M via S and N i.e., TSNM. Therefore, we can conclude that after each half-rotation, the direction of the induced current is reversed. This current is called an alternating current (AC). An AC reverses its direction after equal time intervals.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the principle of an electric generator.
Name some sources of direct current.
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is pushed into the coil?
Explain the underlying principle and working of an electric generator by drawing a labelled diagram. What is the function of brushes?
What type of generator is used at Power Stations?
What is the major difference between the simple alternator and most practical alternators?
Complete the following sentence:
A generator with commutator produces ............... current.
Each one of the following changes will increase emf (or voltage) in a simple generator except:
(a) increasing the number of turns in the armature coil
(b) winding the coil on a soft iron armature
(c) increasing the size of the gap in which the armature turns
(d) increasing the speed of rotation
The current induced in a closed circuit only if there is ______.
What determines the frequency of a.c. produced in a generator?
Draw a labelled diagram of a simple a.c. generator.
What energy conversion does take place in a generator when it is in use?
An a.c. generator changes the ______energy to ______ energy.
State change that you would make to convert an A.C. generator into a D.C. generator. Illustrate the change by a diagram.
The given figures 1 to 3 show the working of a simple A.C. generator. Study the diagrams and answers of the following questions.
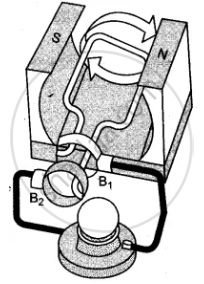
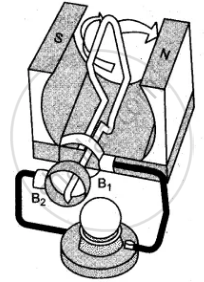
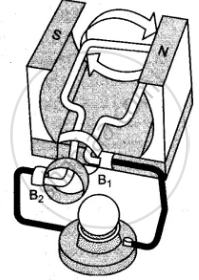
(i) State and explain the principle underlying the working of a simple generator.
(ii) Where is the loop of wire placed?
(iii) What happens when the loop is rotated?
(iv) Indicate the direction of the current flow through the wire for the first half of the turn (in first figure). Name and state the rule used in finding the direction of the current.
(v) Indicate the direction of the current for the case shown in second figure.
(vi) Indicate the direction of current in the outer circuit (i.e., electric bulb) in first and third figure.
(vii) What type of current is shown in the above diagrams? Explain.
Draw and label the diagram of an AC generator.
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer forming a loop and a magnet is:
A: Held stationary
B: Moved away along its axis
C: Moved towards along its axis
D: There will be an induced current in
