Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain how, a karate player can break a pile of tiles with a single blow of his hand.
उत्तर
A karate player can break a pile of tiles with a single blow because he strikes the pile with his hand very fast. In doing so, the large momentum of his hand is reduced to zero in a very short time. This exerts a large force on the pile of tiles which is sufficient to break them apart.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A shell of mass 0.020 kg is fired by a gun of mass 100 kg. If the muzzle speed of the shell is 80 m s–1, what is the recoil speed of the gun?
Explain why, it is easier to stop a tennis ball than a cricket ball moving with the same speed.
Define momentum of a body. On what factors does the momentum of a body depend ?
State the relation between the momentum of a body and the force acting on it.
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
Momentum is a _____________ quantity. Its unit is _____________.
Explain why it is possible for a small animal to fall from a considerable height without any injury being caused when it reaches the ground.
A ball X of mass 1 kg travelling at 2 m/s has a head-on collision with an identical ball Y at rest. X stops and Y moves off. Calculate the velocity of Y after the collision.
A heavy car A of mass 2000 kg travelling at 10 m/s has a head-on collision with a sports car B of mass 500 kg. If both cars stop dead on colliding, what was the velocity of car B ?
Two billiard balls A and B, each of mass 50 g and moving in opposite directions with speed of 5 ms–1 each, collide and rebound with the same speed. If the collision lasts for 10–3 s, which of the following statements are true?
- The impulse imparted to each ball is 0.25 kg ms–1 and the force on each ball is 250 N.
- The impulse imparted to each ball is 0.25 kg ms–1 and the force exerted on each ball is 25 × 10–5 N.
- The impulse imparted to each ball is 0.5 Ns.
- The impulse and the force on each ball are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
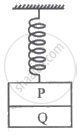
Two blocks P and Q of masses 0.3 kg and 0.4 kg, respectively, are stuck to each other by some weak glue as shown in the figure. They hang together at the end of a spring with a spring constant of k = 200 N/m. The block Q suddenly falls free due to the failure of glue, then the maximum kinetic energy of block P during subsequent motion will be ______ mJ.