Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the principle of dialysis with the help of a labelled diagram.
उत्तर
Principal of dialysis:

The procedure of dialysis is based on diffusion of solutes and ultrafiltration of fluid across a semi-permeable membrane. In dialysis, the blood from a convenient artery is pumped into the dialyser of a dialysing machine. A dialyser contains a coiled cellophane tube surrounded by the dialysing solution. The dialysing solution contains water, glucose and salts, which are similar in concentration to those in normal blood. The porous cellophane membrane of the tube allows the passage of molecules based on concentration gradient. As the patient’s blood is passed through the dialysing solution, most of the wastes (like urea) present in it pass through the selectively permeable cellulose tubes into the dialysing solution, thereby cleaning the blood. The clean blood is pumped back to the body through a vein.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the term haemodialysis.
_____________ secreted by the (ii) _____________ lobe of the pituitary gland. If this hormone secretion is reduced, there is an increased production of urine. This disorder is called (iii) ____________. Sometimes excess glucose is passed with urine due to hyposecretion of another hormone called (iv) _____________ leading to the cause of a disease called (v) ______________.
Name the basic filtration unit present in the kidney.
How are waste products excreted in Amoeba?
Put a tick mark (✓) against the most appropriate alternative in the following statement :
In human beings, urea is produced in :
Answer the following in detail.
Explain the process of transpiration. Describe some factors that affect it.
Differentiate between the following pairs of term :
Renal pelvis and renal papilla
Choose the odd one out in the following serie:
Column of Bertini, minora calyces, brain.
The following diagram represents a mammalian kidney tubule (nephron) and its blood supply.
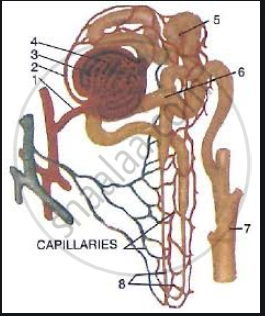
Parts indicated by the guidelines 1to 8 are as follows:
1. Afferent arteriole from renal artery
2. Efferent arteriole
3. Bowman's capsule
4. Glomerulus
5. Proximal convoluted tubule with blood capillaries
6. Distal convoluted tubule with blood capillaries
7. Collecting tubule
8. U-shaped loop of Henle
Study the diagram and answer the question that follow:
Which structure contains the highest concentration of urea?
Study the diagram given alongside and then answer the question that follow:
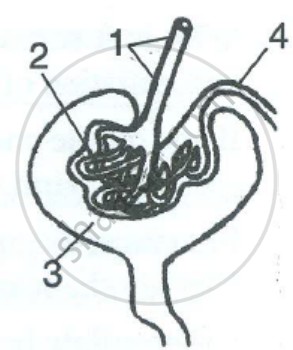
Name the stages involved in the formation of urine.
Study the diagram given alongside and then answer the question that follow:
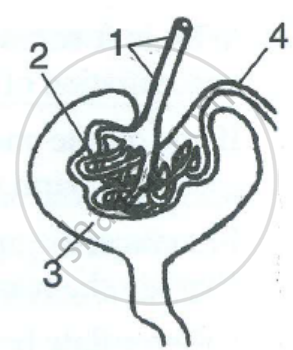
What is the technical term given to the process occurring in 2 and 3? Briefly describe the process.
The diagram below represents a mammalian kidney tubule (nephron) and its blood supply. Parts indicated by the guidelines 1 to 8 are as follows:
1. U-shaped loop of Henle
2. Proximal convoluted tubule with blood capillaries
3. Bowman’s capsule
4. Afferent arteriole from the renal artery
5. Glomerulus
6. Venule to the renal vein
7. Collecting tubule
8. Distal convoluted tubule with blood capillaries Study the diagram and answer the following questions in each case:
(i) Where does ultrafiltration take place?
(ii) Which structure contains the lowest concentration of urea?
(iii) Which structure contains the highest concentration of urea?
(iv) Which structure contains the lowest concentration of glucose?
(v) Where is the most water reabsorbed?
Explain the Term: Glomerulus
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
______ is the functional unit of kidney.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate words:
The outer surface of the kidney is ______ while the inner surface is ______.
Choose the correct option.
The minor calyx _______.
Adult frog is an amphibian, its mode of excretion is ______.
Osmoregulation maintains the osmolarity of blood at about ______.
When uric acid is produced in excess, it gets deposited in joints, resulting in ____________.
“All plants give out oxygen during the day and carbon dioxide during the night”. Do you agree with this statement? Give a reason.
