Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain replication of bacteriophage with the help of a suitable diagram.
उत्तर
the following steps:
- Attachment: Bacteriophages attach to specific receptors on the surface of bacteria. As
phages do not move independently, they rely on random encounters with the right
receptors. - Penetration: After attachment, the tail fibres bring the base plate closer to the surface
of the cell. Once attached completely, the tail contracts, injecting genetic material
(DNA) through the bacterial membrane. (Capsid – protein coat remains outside and is
called ‘ghost’)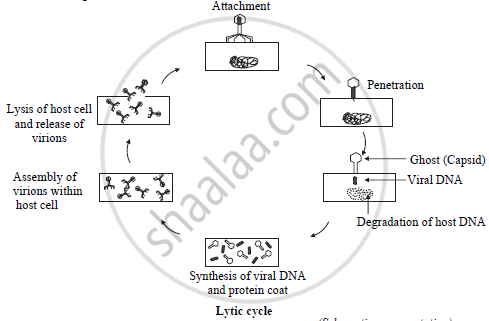
- Degradation of host DNA: Once the viral DNA enters the host cell, the degradation of
host DNA starts. - Synthesis of proteins and nucleic acid: The host’s normal synthesis of proteins and
nucleic acids is disrupted, and it is forced to manufacture viral DNA and proteins
instead. These products are the parts of new virions within the cell or proteins involved
in cell lysis. - Virion assembly: The base plates are assembled with the tails first. The head (capsids)
are constructed separately and then are joined with the tails. The DNA is packed
efficiently within the head. The whole process takes about 15 minutes. - Release of virions: Phages are released via. lysis of cell. It is achieved by an enzyme
called endolysin, which breaks down the cell wall. Released virions are capable of
infecting a new bacterium.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which enzyme does remove supercoils from replicating DNA?
What is the function of SSBP?
For which of the following purpose agarose gel electrophoresis technique is used?
In which direction polymerization of DNA nucleotides occurs during the synthesis of lagging strand?
Which of the following is present at the sticky ends of a fragmented DNA molecule?
Which of the following is the function of single-strand binding proteins?
In DNA molecule, pairing between two complementary nucleotides takes place by ________ bonds.
Okazaki is known for his contribution to the under tanding of:
Identify the biomolecule that is capable of self-replication.
The nucleic acid synthesis takes place in ______.
