Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the term target molecules or drug targets as used in medicinal chemistry.
उत्तर १
In medicinal chemistry, drug targets refer to the key molecules involved in certain metabolic pathways that result in specific diseases. Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids are examples of drug targets.
Drugs are chemical agents designed to inhibit these target molecules by binding with the active sites of the key molecules.
उत्तर २
Drugs interact with macromolecules like proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids thus these macro molecules are called drug targets. These macromolecules perform various functions in the body for example, proteins perform several roles in the body. Proteins which act as biological catalysts are called enzymes, those which are involved in communication system are called receptors. Carrier proteins carry polar molecules across the cell membrane. Nucleic acids have coded genetic information in the cell whereas lipids and carbohydrates form structural part of cell membranes.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define Broad-spectrum antibiotics with a suitable example?
Explain Tranquilizers
Explain the term Antiseptics
Sleeping pills are recommended by doctors to the patients suffering from sleeplessness but it is not advisable to take its doses without consultation with the doctor, Why?
Why do we need to classify drugs in different ways?
Cisplatin compound is used in the treatment of _______.
(A) malaria
(B) cancer
(C) AIDS
(D) yellow fever
Write any ‘two’ side effects of tranquilizers.
Define the following : Narrow spectrum antibiotics
Salvarsan is arsenic-containing drug which was first used for the treatment of ______.
Which of the following is molecular disease?
Parathion is
Which of the following insect species?
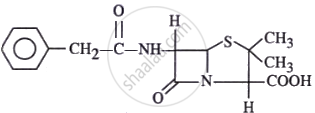
The structure given below is known as
Veronal, a barbituric drug is used as
Antipyretics are medicinal compound and which
Which of the following is NOT a target molecule for drug function in body?
The drug used to get relief from pain are called:
