Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the conventional methods adopted in the vegetative propagation of higher plants.
उत्तर
The common methods of conventional propagation are cutting, grafting, and layering.
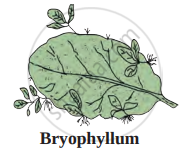
- Cutting: It is the method of producing a new plant by cutting the plant parts such as root, stem, and leaf from the parent plant. The cut part is placed in a suitable medium for growth. It produces roots and grows into a new plant. Depending upon the part used it is called root cutting (Malus), stem cutting (Hibiscus, Bougainvillea, and Moringa), and leaf-cutting (Begonia, Bryophyllum). Stem cutting is widely used for propagation.
- Grafting: In this, parts of two different plants are joined so that they continue to grow as one plant. Of the two plants, the plant which is in contact with the soil is called stock, and the plant used for grafting is called the scion. Examples are Citrus, Mango, and Apple. There are different types of grafting based on the method of uniting the scion and stock. They are bud grafting, approach grafting, tongue grafting, crown grafting, and wedge grafting.
(a) Bud grafting: AT-shaped incision is made in the stock and the bark is lifted. The scion bud with little wood is placed in the incision beneath the bark and properly bandaged with tape.
(b) Approach grafting: In this method both the scion and stock remain rooted. The stock is grown in a pot and it is brought close to the scion. Both of them should have the same thickness. A small slice is cut from both and the cut surfaces are brought near and tied together and held by tape. After 1-4 weeks the tip of the stock and base of the scion is cut off and detached and grown in a separate pot.
(c) Tongue grafting: A scion and stock having the same thickness is cut obliquely and the scion is fit into the stock and bound with tape.
(d) Crown grafting: When the stock is large in size scions are cut into a wedge shape and are inserted on the slits or clefts of the stock and fixed in position using graft wax.(e) Wedge grafting: In this method, a slit is made in the stock, or the bark is cut. A twig of the scion is inserted and tightly bound so that the cambium of the two is joined.
- Layering: In this method, the stem of a parent plant is allowed to develop roots while still intact. When the root develops, the rooted part is cut and planted to grow as a new plant.
Examples: Ixora mdJasminum Mound layering and Air layering are few types of layering.
(a) Mound layering: This method is applied to plants having flexible branches. The lower branch with leaves is bent to the ground and part of the stem is buried in the soil and tip of ( the branch is exposed above the soil. After the roots emerge from the part of the stem buried in the soil, a cut is made in the parent plant so that the buried part grows into a new plant.
(b) Air layering: In this method, the stem is girdled at the nodal region, and hormones are applied to this region which promotes rooting. This portion is covered with damp or moist soil using a; polythene sheet. Roots emerge in these branches after 2-4 months. Such branches are removed from the parent plant and grown in a separate pot or ground.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define vegetative propagation.
What is the modification seen in the Bryophyllum. Explain
List out two sub-aerial stem modifications with examples.
What is layering?
How do Dioscorea reproduce vegetatively?
A detached leaf of Bryophyllum produces new plants. How?
Differentiate Grafting and Layering.
Write short notes on approach grafting.
List down the advantages of conventional methods.
Discuss the importance of Modern methods in the reproduction of plants.
Enumerate the characteristic features of Entomophilous flowers.
Vegetative propagule in Agave is termed as ______
A plant is shown in the given diagram. Identify the plant with its vegetative mode of reproduction.
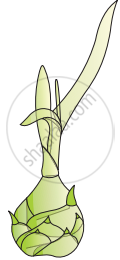
Observe the following figure and answer the questions below:
- Which process is shown in figure?
- Define the process.
- Give an example of the process depicted.
Which ability of plants like banana and bryophyllum is exploited by gardeners and farmers for their commercial propagation?
