Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the structure of secondary oocyte.
उत्तर

The secondary oocyte is the unfertilized egg which is released from the ovary (ovulated).
- Size and structure:
It is non-cleidoic (without shell) and microlecithal (yolk is present in very small quantities). It is approximately 0.1mm (100 microns) in size. It is a rounded, nonmotile, haploid female gamete. The egg shows polarity i.e. the side having a germinal vesicle and the first polar body is called an animal pole while the side opposite to it is called the vegetal pole. - Nucleus:
The nucleus of the egg appears large and is called a germinal vesicle. A typical nucleus or pronucleus is formed at the time of fertilization. - Cytoplasm:
The cytoplasm of the egg is also called ooplasm. It is devoid of centrioles. - Membranes:
The egg is surrounded by various coverings. The egg membrane is called the vitelline membrane. It secretes a non-cellular, glycoproteinous membrane with the zona pellucida on its outside. Adhering to the outer surface of zona pellucida are several radially elongated cells forming the corona radiata. These cells are derived from the innermost layer of granulosa cells. They are firmly held to the zona pellucida and to each other by hyaluronic acid (mucopolysaccharide). Between the vitelline membrane and the zona pellucida is a fluid-filled perivitelline space. The first polar body lies in this space.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis.
At the time of birth, there are _______________ oocytes in the ovary of a female foetus.
The part labelled as ______ contains the energy source that facilitates sperm motility.
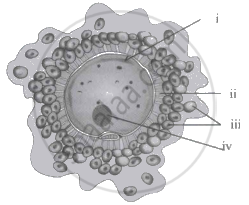
Identify the labels (i-iv) in the given diagram of the ovum.
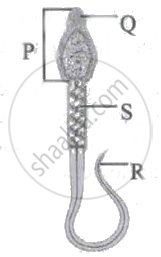
How many functional sperms and how many ova will be formed by a primary spermatocyte and a primary oocyte.
The head of the epididymis at the head of the testis is called ______.
Which of the following are called dual gland?
Mark the odd one.
Process of maturation and development of sperms ______.
Name the germinal layers from which the following organs develop: Tongue, heart, sweat glands, vagina, mammary glands, kidney.
