Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the term Vegetative propagation.
उत्तर
When new plants are produced from the vegetative parts like roots, stems, leaves, and buds it is known as vegetative propagation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Yeast reproduces by _________.
(a) spore formation
(b) multiple fission
(c) fragmentation
(d) budding
Draw labelled diagrams to illustrate budding in Hydra.
A student has to focus his compound microscope to observe a prepared slide showing different stages of binary fission in Amoeba. The steps he is likely to follow are listed below in a haphazard manner:
I. Adjust the diaphragm and the mirror of the microscope so that sufficient light may enter to illuminate the slide.
II. Fix the slide on the stage carefully.
III. Adjust the microscope to high power and focus.
IV. Adjust the microscope to low power and focus.
The correct sequence of the above steps to observe the slide under the microscope is
(A) I, II, IV, III
(B) II, I, IV, III
(C) II, IV, I, III
(D) I, IV, II, III
Study the following diagrams showing various stages of binary fission in Amoeba:
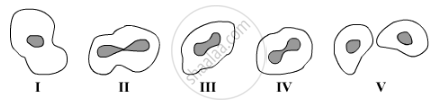
The correct sequence of these diagrams should be:
(A) I, IV, III, II, V
(B) I, III, IV, II, V
(C) I, II, IV, III, V
(D) I, II, III, IV, V
Can you think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration?
What happens when On maturation sporangia of Rhizopus bursts?
Name the process by which an Amoeba reproduces. Draw the various stages of its reproduction in a proper sequence.
A student in viewing under a microscope a permanent slide showing various stages of asexual reproduction by budding in yeast. Draw diagrams of what he observes (in proper sequence)
State whether the following statement is true or false :
Spores produced by the bread mould plant are actually its seeds.
Describe the layering method for the artificial propagation of plants. Illustrate your answer with the help of a labelled diagram. Name any five plants which are propagated by the layering method.
What is a tuber? Name one stem tuber and one root tuber.
Name two organisms which reproduce by the same asexual process as that of Amoeba.
A worm X found in freshwater and slow-moving streams has been accidently cut into three pieces. It was observed that in due course of time, each cut piece of the worm develops to become a complete worm by growing all the missing parts.
(a) Name the worm X which can exhibit this phenomenon of making complete worm from its cut body parts.
(b) Name another organism Y which possesses the same characteristic of growing fully from its cut body parts.
(c) What is the name of this process in which a complete organism is formed from its cut body part.
(d) State whether X and Y are unicellular and/or multicellular organisms.
(e) Can a dog be produced completely form its cut body part (say, a cut tail) just like organisms X and Y? Why?
Put a tick mark (✓) against the correct alternative in the following statement
Grafting is a method of:
Briefly explain why a gardener prefers to grow certain plants vegetatively?
Why is it disadvantageous to grow plants vegetatively?
Multiple choice question. Tick (✓) the correct choice:
Budding is commonly seen in
- yeast
- grasses
- Amoeba
- Spirogyra
Differentiate between the following:
Cutting and grafting
Define the following:
Vegetative reproduction
Mention the common method of reproduction in Bougainvillea.
Describe the advantages of vegetative reproduction.
A blue colour flower plant denoted by BB is crossbred with that of white colour flower plant denoted by bb.
(a) State the colour of flower you would expect in their F1 generation plants.
(b) What must be the percentage of white flower plants in F2 generation if flowers of F1 plants are self-pollinated?
(c) State the expected ratio of the genotypes BB and Bb in the F2 progeny.
From the following diagrams, select the correct ones showing stages of binary fission in Amoeba:
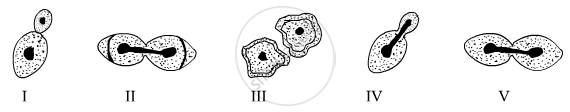
(A) I, II, III
(B) IV, II, III
(C) V, II, III
(D) IV, I, III
Following diagrams were drawn by different student on having seen prepared slides of budding in yeast.
Correct diagrams are
(A) I, II, III
(B) II, III, IV
(C) III, IV, V
(D) I, IV, V
Name a multicellular organism which reproduces by fragmentation method.
A student was given two permanent slides, one of binary fission in Amoeba and other of budding in yeast. He was asked to identify any one difference in the nucleus of the two. One such difference, he identified correctly was
(1) Presence of one nucleus in Amoeba, two in yeast cell and one in bud.
(2) Presence of two nuclei in centrally constricted Amoeba, one in yeast cell and one in its bud.
(3) Presence of two distant nuclei in Amoeba, one in yeast cell and two in bud.
(4) Presence of a single nucleus each in Amoeba, yeast cell and its attached bud.
Name the mode of reproduction process seen in yeast.
List in tabular form two differences between binary fission and multiple fission.
Name the parts of the plants used to grow following flower: Lily
Give the name of the plant that reproduces vegetatively by: Underground stem
How is plant hybridisation carried out?
Name the hormone produced by unfertilised ovary responsible for enlargement of ovary into fruit.
Which of the following is not a type of asexual reproduction in multicellular organisms?
Name the three types of asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms.
- Which type of reproduction is indicated in the following diagram?
- Redraw the given type of reproduction in the correct sequence and explain it.

The asexual reproduction in bacteria occurs by ______.
In Spirogyra, asexual reproduction takes place by
Can you consider cell division as a type of reproduction in unicellular organism? Give one reason.
The symbiotic association between fungi and algae is called ______.
