Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the various phases of the menstrual cycle.
उत्तर
Menstrual cycle: The menstrual or ovarian cycle occurs approximately once in every 28/29 days during the reproductive life of the female from menarche (puberty) to menopause except during pregnancy. The cycle of events starting from one menstrual period till the next one is called the menstrual cycle during which cyclic changes occur in the endometrium every month. Cyclic menstruation is an indicator of normal reproductive phase.
Menstrual cycle comprises of the following phases:
- Menstrual phase
- Follicular or proliferative phase
- Ovulatory phase
- Luteal or secretory phase
1. Menstrual phase: The cycle starts with the menstrual phase when menstrual flow occurs and lasts for 3-5 days. Menstrual flow is due to the breakdown of endometrial lining of the uterus, and its blood vessels due to decline in the level of progesterone and oestrogen. Menstruation occurs only if the released ovum is not fertilized. Absence of menstruation may be an indicator of pregnancy. However it could also be due to stress, hormonal disorder and anaemia.
2. Follicular or proliferative phase: The follicular phase extends from the 5th day of the cycle until the time of ovulation. During this phase, the primary follicle in the ovary grows to become a fully mature Graafian follicle and simultaneously, the endometrium regenerates through proliferation. These changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by the secretion of gonadotropins like FSH and LH, which increase gradually during the follicular phase. It stimulates follicular development and secretion of oestrogen by the follicle cells.
3. Ovulatory phase: Both LH and FSH attain peak level in the middle of the cycle (about the 14th day). Maximum secretion of LH during the mid-cycle called LH surge induces the rupture of the Graafian follicle and the release of the ovum (secondary oocyte) from the ovary wall into the peritoneal cavity. This process is called as ovulation.
4. Luteal or secretory phase: During luteal phase, the remaining part of the Graafian follicle is transformed into a transitory endocrine gland called corpus luteum. The corpus luteum secretes large amount of progesterone which is essential for the maintenance of the endometrium. If fertilization takes place, it paves way for the implantation of the fertilized ovum.
The uterine wall secretes nutritious fluid in the uterus for the foetus. So, this phase is also called as secretory phase. During pregnancy all events of menstrual cycle stop and there is no menstruation. In the absence of fertilization, the corpus luteum degenerates completely and leaves a scar tissue called corpus albicans. It also initiates the disintegration of the endometrium leading to menstruation, marking the next cycle.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the role of hormones during the menstrual cycle.
Multiple choice question.
Rupturing of follicles and discharge of ova is known as _______.
What are the phases of the menstrual cycle? Indicate the changes in the ovary and uterus.
The following is the illustration of the sequence of ovarian events (a-i) in a human female.
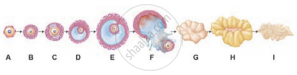
Explain the changes that occur in the uterus simultaneously in anticipation.
Menstruation begins due to ______.
Ovulation in the human female normally takes place during the menstrual cycle ______.
Corpus luteum develops from ______.
A human female reaches menopause aroung the age of ______.
A biology student after studying the different levels of hormones during the menstrual cycle was comparing 2 subjects (Patients). A table was created after looking at the levels of hormones A and B for Subjects 1 and 2. Read the information in the table and answer the question that follows.
| HORMONE A | HORMONE B | |
| Subject 1 | Shows a peak on the 14th Day of the menstrual cycle. | Falls down during the luteal phase. |
| Subject 2 | Shows a peak on the 14th Day of the menstrual cycle. | The level is maintained high in the luteal phase. |
Which structure in the ovary will remain functional in subject 2?
Which of the following events is not associated with ovulation in human females?
The main function of mammalian corpus luteum is to produce ______.
The secretory phase in the human menstrual cycle is also called:
About which day in a normal human menstrual cycle does rapid secretion of LH (Popularly called LH Surge) normally occurs?
After ovulation the collapsed ovarian follicle shrinks and becomes filled with cell to form:
What are the events taking place in the ovary and uterus during follicular phase of the menstrual cycle.
Spermatogenesis is induced by ______.
Name the following:
The permanent stoppage of menstruation in human females around the age of 45 years.
Given below is a group of terms. In the group, one pair indicates the relationship between the two terms. Rewrite and complete the second pair on a similar basis.
Follicular phase: 5-12 days:: Luteal phase : ______ days.
Complete the following table by writing the name of the structure or the function of the given structure:
| Structure | Function | ||
| 1. | Corpus luteum | 1. | ______ |
| 2. | ______ | 2. | Produces male gametes in mass |
| 3. | Leydig cells | 3. | ______ |
| 4. | ______ | 4. | Stores the sperms until they mature and become mobile |
| 5. | Umbilical cord | 5. | ______ |
| 6. | Fallopian tube | 6. | ______ |
