Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain water cycle in detail.
उत्तर
It represents the exchange of water between air, land and sea and between the living organisms and the environment.
Two overlapping water cycles are operating in nature:
(i) Global water cycle-
Water evaporates from the hydrosphere (oceans, lakes, rivers seas, ponds) by the heat of the sun and forms clouds. Clouds are carried over to the land by winds. After getting cooled, water in the clouds falls on the earth in the form of rain, sleet and hail. This water again evaporates in the atmosphere and completes the global water cycle.
(ii) Biological water cycle-
Here, the living organisms, i.e., plants and animals, consume water from the global water cycle and return it back. Plants release water in the form of water vapours by the process of transpiration. Animals return water to the air as vapours by the process of respiration and to the soil in the form of fluid by the process of excretion.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
During winters why do we see more fog in close areas where there are lots of trees?
What happens to the water in a wet cloth?
Water becoming water vapour on heating is called evaporation.
What are the processes involved in water cycle?
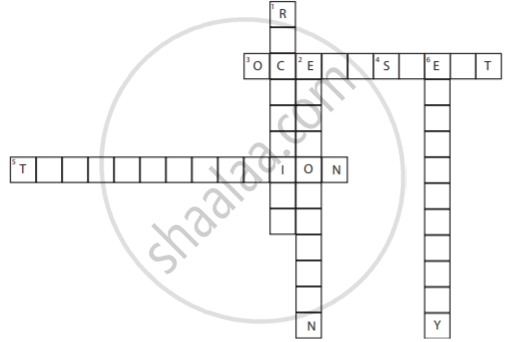
CROSSWORD
DOWN
1. A method of water conservation.
2. Process of getting water vapour from sea water.
6. Water stored in dams is used for the generation of ______.
ACROSS
3. is a large body of non-potable water found in nature.
4. In summer, the body loses water as ______.
5. Plants undergo ______ and contribute to the water cycle.
State for the following whether it is due to evaporation or condensation:
Steam rising from wet clothes while they are ironed.
In plants, the loss of water in the form of vapour from the aerial parts through ______.
The water vapour gets cooled and changes into tiny water droplets that form ______ in the sky.
“Catch water where it falls” is the basic idea behind
The cyclic flow of nutrients between non-living and living factors of the environment is termed as ______ cycle.
