Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Fig. shows two rays of light Op and OQ coming from an object at the bottom of a pond, incident on the water surface.
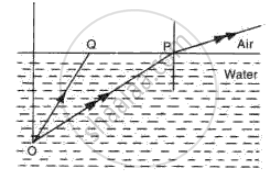
(a) Mark on the diagram
(i) The angle of incidence of ray OP,
(ii) The angle of refraction of ray Op,
(iii) The position of image of the object as seen from above.
(iv) An approximate path of the ray OQ.
(b) Explain, why do the rays of light change directions on passing from water to air.
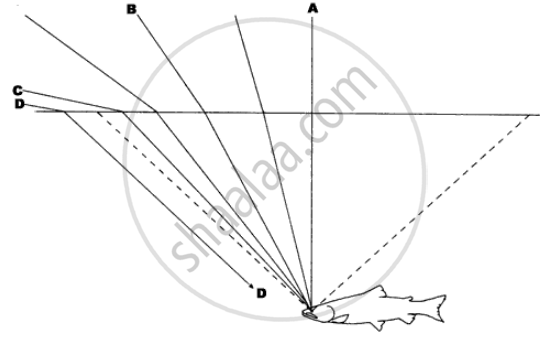
(c) A fish in water sees everything outside the water by rays of light entering its eye in a small cone of light. Draw a diagram and explain how does this happen.
उत्तर

(i) Angle of incidence (i) of ray OP is marked in the above diagram.
(ii) Angle of refraction (r) of ray OP is marked in the above diagram.
(iii) The position of image of the object (O') as seen from above is marked in the diagram.
(iv) An approximate path of ray OQ is shown in the above diagram.
(b) Water is a denser medium as compared to air; so on passing from water (denser) to air (rarer) the speed of light of light increases and it bends away from the normal.
(c)
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from a medium of one optical density into a medium of a different optical density, as from air to water or water into air. The amount of bending is dependent upon the incident angle of the light. In the diagram below, a light ray, "A" strikes the water at right angles and passes through the surface without bending. But as the incident angle decreases (becomes less than 90 degrees) the light bends more and morerays "B" and "C." Light striking the surface parallel to the surface, bends downward.
Since light is coming into the water from all directions, refraction creates a cone of light with its base on the surface and its apex at the fish's eye. The base of the cone is a circular opening at the surface through which the fish sees the entire outside world. This opening is called the "Fish's Window". Only the light passing through the window enters the fish's eye. Notice line "D," It's a ray entering the water beyond the window; refraction bends it such that it cannot reach the fish's eye.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Study the diagram shown in Fig. 5.56
Complete the diagram to show the formation of image A’B’ of the object AB of same size.
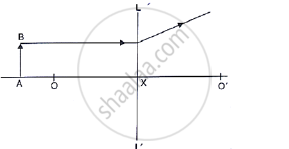
Study the diagram shown in Fig. 5.56
where is the object located?
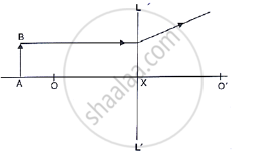
State the condition of the following:
A ray passes undeviated through the lens.
In the following diagram the object and the image formed by the respective lenses are shown. Complete the ray diagram, and locate the focus. Find the focal length of the lens.
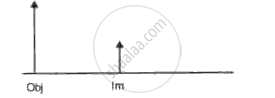
Make the correct choices in the following items :
A lens used as a magnifying glass
(i) ls a diverging lens
(ii) Produces a virtual image
(iii) ls placed with the object nearer the lens than the principle focus
Make the correct choices in the following items:
lf the image can be focused on a screen it must be
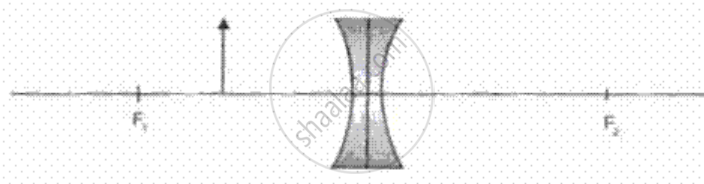
Make the correct choices in the following items :
The image formed by a diverging lens, shown in fig, , is
How will you differentiate between a convex and a concave lens by looking at a printed page?
Draw a ray diagram to show the image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed between F and 2F.
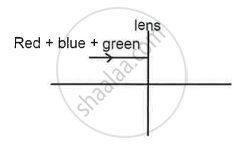
Mixture of red + blue + green is passed through a convex lens as shown in the diagram below. State whether the ray passes through a single point or through different points on the principal axis after refraction.