Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Figure shows the position-time graph of a body of mass 0.04 kg. Suggest a suitable physical context for this motion. What is the time between two consecutive impulses received by the body ? What is the magnitude of each impulse ?

उत्तर १
A ball rebounding between two walls located between at x = 0 and x = 2 cm; after every 2 s, the ball receives an impulse of magnitude 0.08 × 10–2 kg m/s from the walls
The given graph shows that a body changes its direction of motion after every 2 s. Physically, this situation can be visualized as a ball rebounding to and fro between two stationary walls situated between positions x = 0 and x = 2 cm. Since the slope of the x-t graph reverses after every 2 s, the ball collides with a wall after every 2 s.
Therefore, ball receives an impulse after every 2 s.
Mass of the ball, m = 0.04 kg
The slope of the graph gives the velocity of the ball. Using the graph, we can calculate initial velocity (u) as:
`u = ((2-0)xx10^2)/(2-0) = 10^(-2) "m/s"`
Velocity of the ball before collision, u = 10–2 m/s
Velocity of the ball after collision, v = –10–2 m/s
(Here, the negative sign arises as the ball reverses its direction of motion.)
Magnitude of impulse = Change in momentum
=|mv - mu|
=|0.04 (v -u)|
=|`0.04(-10^(-2)- 10^(-2))`|
= 0.08 × 10–2 kg m/s
उत्तर २
This graph can be of a ball rebounding between two walls situated at position 0 cm and 2 cm. The ball is rebounding from one wall to another, time and again every 2 s with uniform velocity.
Impulse, Here velocity = `("displacement")/"time" = 2/(100xx2) = 0.01 ms^(-2)`
Initial momentum = mu = `0.04 xx 0.01 = 4 xx 10^(-4) "kg ms"^(-1)`
Final momentum = mv = `0.04 x (-0.01) = -4 xx 10^(-4) "kg ms"^(-1)`
Magnitude of impulse = Change in momentum
=`(4xx 10^(-4)) -(-4xx10^(-4)) = 8 xx 10^(-4) kg ms^(-1)`
Time between two consecutive impulses is 2 s.i.e the ball receive an impulse every 2 s
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two billiard balls, each of mass 0.05 kg, moving in opposite directions with speed 6 ms-1collide and rebound with the same speed. What is the impulse imparted to each ball due to the other?
Figure shows a man standing stationary with respect to a horizontal conveyor belt that is accelerating with 1 m s–2. What is the net force on the man? If the coefficient of static friction between the man’s shoes and the belt is 0.2, up to what acceleration of the belt can the man continue to be stationary relative to the belt? (Mass of the man = 65 kg.)

A stream of water flowing horizontally with a speed of 15 m s–1 gushes out of a tube of cross-sectional area 10–2 m2, and hits a vertical wall nearby. What is the force exerted on the wall by the impact of water, assuming it does not rebound?
Explain why, it is easier to stop a tennis ball than a cricket ball moving with the same speed.
Name the principle on which a rocket works.
A body of mass 2 kg is at rest. What should be the magnitude of force which will make the body move with a speed of 30 m/s at the end of 1 s ?
State the law of conservation of momentum.
The troops (soldiers) equipped to be dropped by parachutes from an aircraft are called paratroopers. Why do paratroopers roll on landing ?
Two billiard balls A and B, each of mass 50 g and moving in opposite directions with speed of 5 ms–1 each, collide and rebound with the same speed. If the collision lasts for 10–3 s, which of the following statements are true?
- The impulse imparted to each ball is 0.25 kg ms–1 and the force on each ball is 250 N.
- The impulse imparted to each ball is 0.25 kg ms–1 and the force exerted on each ball is 25 × 10–5 N.
- The impulse imparted to each ball is 0.5 Ns.
- The impulse and the force on each ball are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
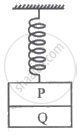
Two blocks P and Q of masses 0.3 kg and 0.4 kg, respectively, are stuck to each other by some weak glue as shown in the figure. They hang together at the end of a spring with a spring constant of k = 200 N/m. The block Q suddenly falls free due to the failure of glue, then the maximum kinetic energy of block P during subsequent motion will be ______ mJ.