Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the diameter of the image of the moon formed by a spherical concave mirror of focal length 7.6 m. The diameter of the moon is 3450 km and the distance between the earth and the moon is 3.8 × 105 km.
उत्तर
Given,
Focal length of the concave mirror, f = − 7.6 m
Distance between earth and moon taken as object distance, u = −3.8 × 105 km
Diameter of moon = 3450 km
Using mirror equation:
\[\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v} = \frac{1}{u} + \frac{1}{f}\]
\[\therefore \frac{1}{v} + \left( - \frac{1}{3 . 8 \times {10}^8} \right) = \left( - \frac{1}{7 . 6} \right)\]
As we know, the distance of moon from earth is very large as compared to focal length it can be taken as ∞.
Therefore, image of the moon will be formed at focus, which is inverted.
\[\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v} = - \frac{1}{7 . 6}\]
⇒ v = −7.6 m
We know that magnification is given by:
\[m = - \frac{v}{u} = \frac{d_{image}}{d_{object}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \frac{- ( - 7 . 6)}{( - 3 . 8 \times {10}^8 )} = \frac{d_{image}}{3450 \times {10}^3}\]
\[d_{image} = - \frac{3450 \times 7 . 6 \times {10}^3}{3 . 8 \times {10}^8}\] = \[-\] 0.069 m = -6.9 cm
Hence, the required diameter of the image of moon is 6.9 cm.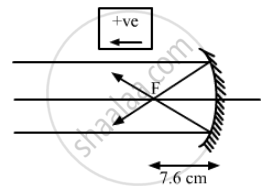
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object is placed 15 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. Find the nature and position of the image formed. Where should a concave mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm be placed so that the final image is formed at the position of the object itself?
A mobile phone lies along the principal axis of a concave mirror. Show, with the help of a suitable diagram, the formation of its image. Explain why magnification is not uniform.
Suppose the lower half of the concave mirror's reflecting surface is covered with an opaque material. What effect this will have on the image of the object? Explain
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm is placed coaxially with a convex mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm. The two are kept 15 cm apart. A point object is placed 40 cm in front of the convex lens. Find the position of the image formed by this combination. Draw the ray diagram showing the image formation.
Obtain the mirror formula and write the expression for the linear magnification.
A convex lens of focal length 25 cm is placed coaxially in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm. Determine the power of the combination. Will the system be converging or diverging in nature?
A convex lens of focal length 30 cm is placed coaxially in contact with a concave lens of focal length 40 cm. Determine the power of the combination. Will the system be converging or diverging in nature?
A convex lens of focal length f1 is kept in contact with a concave lens of focal length f2. Find the focal length of the combination.
An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure.
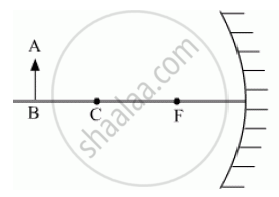
(i) Complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object.
(ii) How will the position and intensity of the image be affected if the lower half of the mirror’s reflecting surface is painted black?
A hemispherical portion of the surface of a solid glass sphere (μ = 1.5) of radius r is silvered to make the inner side reflecting. An object is placed on the axis of the hemisphere at a distance 3r from the centre of the sphere. The light from the object is refracted at the unsilvered part, then reflected from the silvered part and again refracted at the unsilvered part. Locate the final image formed.
The convex surface of a thin concavo-convex lens of glass of refractive index 1.5 has a radius of curvature 20 cm. The concave surface has a radius of curvature 60 cm. The convex side is silvered and placed on a horizontal surface as shown in figure. (a) Where should a pin be placed on the axis so that its image is formed at the same place? (b) If the concave part is filled with water (μ = 4/3), find the distance through which the pin should be moved so that the image of the pin again coincides with the pin.
A particle is moving at a constant speed V from a large distance towards a concave mirror of radius R along its principal axis. Find the speed of the image formed by the mirror as a function of the distance x of the particle from the mirror.
A small block of mass m and a concave mirror of radius R fitted with a stand lie on a smooth horizontal table with a separation d between them. The mirror together with its stand has a mass m. The block is pushed at t = 0 towards the mirror so that it starts moving towards the mirror at a constant speed V and collides with it. The collision is perfectly elastic. Find the velocity of the image (a) at a time t < d/V, (b) at a time t > d/V.
A gun of mass M fires a bullet of mass m with a horizontal speed V. The gun is fitted with a concave mirror of focal length f facing towards the receding bullet. Find the speed of separation of the bullet and the image just after the gun was fired.
Two concave mirrors of equal radii of curvature R are fixed on a stand facing opposite directions. The whole system has a mass m and is kept on a frictionless horizontal table following figure. Two blocks A and B, each of mass m, are placed on the two sides of the stand. At t = 0, the separation between A and the mirrors is 2 R and also the separation between B and the mirrors is 2 R. The block B moves towards the mirror at a speed v. All collisions which take place are elastic. Taking the original position of the mirrors-stand system to be x = 0 and X-axis along AB, find the position of the images of A and B at t = (a) `R/v` (b) `3R/v` (c) `5R/v`.

In the case of a concave mirror of focal length f , when an object is kept between f and 2 f , show that its image is formed beyond 2 f .
