Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the effective resistance in the following circuit diagrams (Fig.):
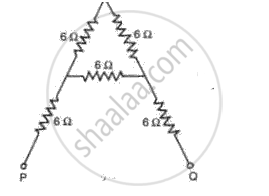
उत्तर
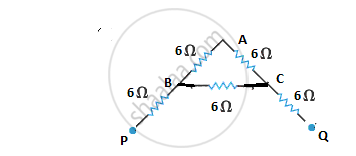
In the given network, between B and C the series combination
of two 6 Ω resistors is connected in parallel with the third 6Ω resistor.
`1/"R"_"equivalent" = 1/(6 +6) + 1/6 = 1/12 + 1/6 = 3/12 = 1/4`
`"R"_"equivalent" = 4 Omega`
Now, between P and Q, two 6 Ω resistors and 4Ω resistor are connected in series.
:. total resistance between P and Q is:
`"R"_"total"` = 6 + 6 + 4 = 16Ω
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How many milliamperes as there in 1 ampere?
V1, V2 and V3 are the p.ds. across the 1Ω, 2Ω and 3Ω resistors in the following diagram, and the current is 5 A.
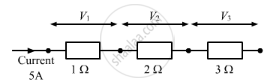
Which one of the columns (a) to (d) shows the correct values of V1, V2 and V3measured in volts?
`V_1` `V_2` `V_3`
(a) 1.0 2.0 3.0
(b) 5.0 10.0 15.0
(c) 5.0 2.5 1.6
(d) 4.0 4.0 2.0
Consider the circuit given below when A, B and C are three identical light bulbs of constant resistance. 
(a) List the bulbs in order of increasing brightness.
(b) If C burns out, what will be the brightness of A now compared with before?
(c) If B burns out instead, what will be the brightness of A and C compared with before?
The rating of a fuse connected in the lighting circuit is:
(a) 15 A (b) 5 A (c) 10 A (d) Zero
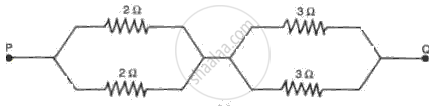
Find the effective resistance in the following circuit diagrams (Fig.):
Three heaters each rated 250 W, 100 V are connected in parallel to a 100 V supply of the energy supplied in kWh to the three heaters in 5 hours.
Answer the following question.
An electric lamp of resistance 20 Ω and a conductor of resistance 4 0 are connected to a 6 V battery as shown in the circuit. Calculate: 
(a) the total resistance of the circuit,
(b) the current through the circuit,
(c) the potential difference across the (i) electric lamp and (ii) conductor, and
(d) power of the lamp.
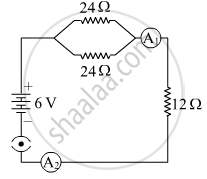
Study the following circuit and find out:
(i) Current in 12 Ω resistor.
(ii) The difference in the readings of A1 and A2, if any.
The power of an electric device is a product of ______ and ______.
Conventionally, the direction of the current is taken as:
