Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the odd one out:
पर्याय
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
Expansion
उत्तर
Expansion
Explanation:
Conduction, convection, and radiation are all ways of heat transport, whereas material expansion is a property.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What do you understand by the following statements:
The specific heat capacity of lead is 130 Jkg-1K-1.
A copper vessel of mass 100 g contains 150 g of water at 50°C. How much ice is needed to cool it to 5°C?
Given: Specific heat capacity of copper = 0.4 Jg-1 °C-1
The Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 Jg-1 °C-1
The Specific latent heat of fusion ice = 336 Jg-1
Specific heat capacity of substance A is 3.8 J g-1K-1 whereas the specific heat capacity of substance B is 0.4 J g-1 K-1
(i) Which of the two is a good conductor of heat?
(ii) How is one led to the above conclusion?
(iii) If substances A and B are liquids then which one would be more useful in car radiators?
Heat supplied to a solid change it into liquid. What is this change in the phase called?
It is generally cold after a hail-storm then during and before the hail storm. Give reason.
Explain the meaning of green house effect.
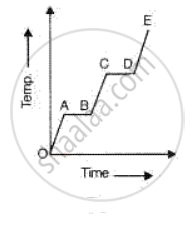
A substance is heated at a constant rate from a low temperature to a high temperature. A graph of temperature against time is shown in the figure. Which part or parts of the graph correspond(s) to the substance existing in two states?
Specific heat capacity of a substance A is 3.8 J g-1 K-1 and of substance B is 0.4 J g-1 k-1. Which substance is a good conductor of heat? How did you arrive at your conclusion?
A liquid X has specific heat capacity higher than the liquid Y. Which liquid is useful as coolant in car radiators.
Does the specific heat capacity of a substance depend upon its mass and rise in temperature only?
Explain, why is water sprayed on roads in evening in hot summer?
A certain amount of heat Q will warm 1 g of material X by 3°C and 1 g of material Y by 4°C. Which material has a higher specific heat capacity?
1 kg of water freezes to form ice at 0°C. What amount of heat is withdrawn?
A substance is in the form of a solid at 0°C. The amount of heat added to this substance and the temperature of the substance are plotted on the following graph:

If the specific heat capacity of the solid substance is 500 J/kg °G, find from the graph, the mass of the substance.
A piece of iron of mass 2.0 kg has a thermal capacity of 966 J/°C. What is its specific heat capacity in S.I. units?
The specific heat capacity of water is 1 cal/g °C.
A monoatomic gas of pressure 'P' having volume 'V' expands isothermally to a volume '2V' and then adiabatically to a volume '16V'. The final pressure of the gas is ______.
(ratio of specific heats = `5/3`)
Heat is applied to a rigid diatomic gas at constant pressure. The ratio ΔQ : ΔU : ΔW is ______.
If 'f' is the number of degrees of freedom of a molecule of a gas and ratio of molar specific heats of a gas, ϒ = 1 + `2/"f"` where ϒ = Cp/Cv. The ratio of 'ϒ' for monoatomic gas to 'ϒ' for (rigid) f diatomic gas is ______.
On supplying 100 µC of charge to a conductor, its potential rises by 5 V then capacity of the conductor is ______.
