Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Four alternative answers for the following question is given. Choose the correct alternative.
Two circles of radii 5.5 cm and 4.2 cm touch each other externally. Find the distance between their centres
पर्याय
9.7
1.3
2.6
4.6
उत्तर
Let the two circles having centres P and R touch each other externally at point Q.
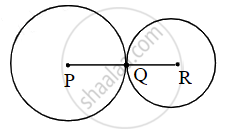
Here, PQ = 5.5 cm, QR = 4.2 cm
The two circles touch each other externally. ...(P−Q−R)
If the circles touch each other externally, distance between their centres is equal to the sum of their radii.
∴ By theorem of touching circles,
∴ PR = PQ + QR
∴ PR = 5.5 + 4.2
∴ PR = 9.7 cm
∴ The distance between the centres of the circles is 9.7 cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If two circles with radii 5 cm and 3 cm respectively touch internally, find the distance between their centres.
If two circles with radii 8 cm and 3 cm respectively touch externally, then find the distance between their centres.
Two circles having radii 3.5 cm and 4.8 cm touch each other internally. Find the distance between their centres.
If radii of two circles are 4 cm and 2.8 cm. Draw a figure of this circles touching each other externally.
Four alternative answers for the following question is given. Choose the correct alternative.
A circle touches all sides of a parallelogram. So the parallelogram must be a, ______
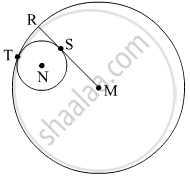
In the given figure, circle with centre M touches the circle with centre N at point T. Radius RM touches the smaller circle at S. Radii of circles are 9 cm and 2.5 cm. Find the answers to the following questions hence find the ratio MS:SR.
(1) Find the length of segment MT
(2) Find the length of seg MN
(3) Find the measure of ∠NSM.
In the adjoining figure circles with centres X and Y touch each other at point Z. A secant passing through Z intersects the circles at points A and B respectively. Prove that, radius XA || radius YB. Fill in the blanks and complete the proof.
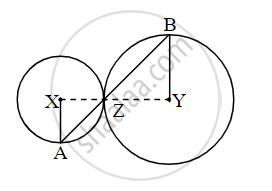
Construction: Draw segments XZ and YZ.
Proof:
By theorem of touching circles, points X, Z, Y are `square`.
∴ ∠XZA ≅ `square` ...(opposite angles)
Let ∠XZA = ∠BZY = a ...(I)
Now, seg XA ≅ seg XZ ...[Radii of the same circle]
∴∠XAZ = `square` = a ...[isosceles triangle theorem](II)
Similarly,
seg YB ≅ seg YZ ...[Radii of the same circle]
∴∠BZY = `square` = a ...[isosceles triangle theorem](III)
∴ from (I), (II), (III),
∠XAZ = `square`
∴ radius XA || radius YZ ...[`square`]
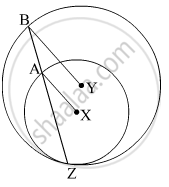
In the given figure, circles with centres X and Y touch internally at point Z . Seg BZ is a chord of bigger circle and it itersects smaller circle at point A. Prove that, seg AX || seg BY.
Draw circles with centres A, B and C each of radius 3 cm, such that each circle touches the other two circles.
In the given figure, circles with centres C and D touch internally at point E. D lies on the inner circle. Chord EB of the outer circle intersects inner circle at point A. Prove that, seg EA ≅ seg AB.

If two circles with diameters 8 cm and 6 cm respectively touch externally, find the distance between their centers.
Two circles of radii 5.5 cm and 3.3 cm respectively touch each other externally. What is the distance between their centres?
Four alternative answers for the following question is given. Choose the correct alternative.
Two circles having diameters 8 cm and 6 cm touch each other internally. Find the distance between their centres.
Line ℓ touches a circle with centre O at point P. If radius of the circle is 9 cm, answer the following.
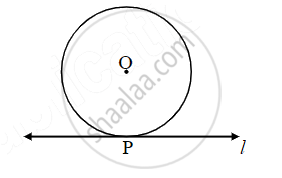
What is d(O, P) =? Why?
Line ℓ touches a circle with center O at point P. If the radius of the circle is 9 cm, answer the following.
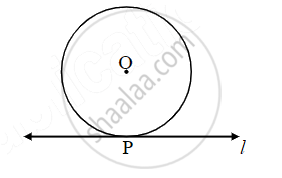
If d(O, Q) = 8 cm, where does the point Q lie?
Line ℓ touches a circle with centre O at point P. If radius of the circle is 9 cm, answer the following.

If d(O, R) = 15 cm, how many locations of point R are line on line l? At what distance will each of them be from point P?
A circle with centre P is inscribed in the ∆ABC. Side AB, side BC, and side AC touch the circle at points L, M, and N respectively. The radius of the circle is r.
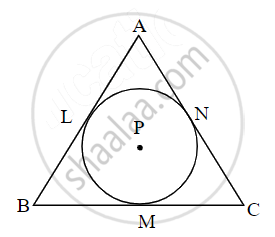
Prove that: A(ΔABC) = `1/2` (AB + BC + AC) × r
