Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
| ALVEOLI OF INFANT | ALVEOLI OF ADULT |
| 1. Alveoli of the infant is thin and tubular. | 1. Alveoli of the adult is thick and sac-like. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
During respiration there is
What are the functions of the following in breathing?
Ribs
What are the functions of the following in breathing?
Abdominal muscles
The volume of air in the lungs and the rate at which it is exchanged during inspiration and expiration was measured.
The following diagram shows a group of the lung volumes and capacities.
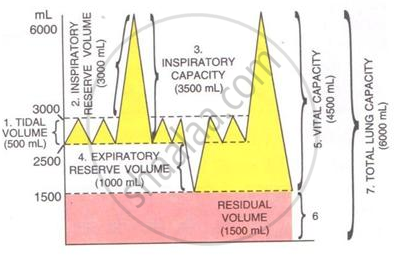
Study the diagram carefully and explain briefly the following :
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
The front opening of the wind pipe is guarded by ______.
Name the following:
The microscopic air-sacs of the lungs.
Name the following:
The two membranes which protect the lungs.
Why is the respiratory system necessary?
Differentiate between
bronchi and alveoli.
Find the odd one out. Give a reason for your choice.
tannin, urine, latex, resin
Name the following:
Sound producing organ.
Complete the following statement by choosing the correct alternative from those given below.
Net gain of complete cellular respiration of carbohydrate ______.
Give the functions of the following:
Alveoli
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
During respiration, the diaphragm
Match the following.
| 1. | Digestive System | Kidney |
| 2. | Respiratory system | Brain |
| 3. | Circulatory system | Alimentary canal |
| 4. | Excretory system | Heart |
| 5. | Nervous System | Lungs |
Which of the following has a set of lymphoid organs called tonsils?
Pick the odd one out from each of the groups given below on the basis of respiratory organs. Give a reason for your answer.
lizard, cow, earthworm, snake
Match the following
| i. | Alveoli | a. | Yeast |
| ii. | Ethanol | b. | Gaseous exchange |
| iii. | Diffusion | c. | Amino acids |
| iv. | Protein | d. | Perfume |
What is the significance of ciliated epithelium present in the nostrils?
For completion of respiration process, write the given steps in sequential manner
- Diffusion of gases (O2 and CO2) across alveolar membrane.
- Transport of gases by blood.
- Utilisation of O2 by the cells for catabolic reactions and resultant release of CO2.
- Pulmonary ventilation by which atmospheric air is drawn in and CO2 rich alveolar air is released out.
- Diffusion of O2 and CO2 between blood and tissues.
