Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given alongside is a diagram of a smear of human blood. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
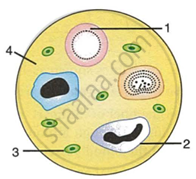 |
- Name the parts l, 2, 3 and 4 indicated by guidelines.
- Mention two structural differences between the parts labelled 'l' and '2'.
- What is the main function of the parts labelled 1, 2 and 3 respectively?
- What is the life span of the part labelled '1'?
- Name a soluble protein found in '4' which helps in the clotting of blood.
उत्तर
-
- RBC's (Erythrocytes)
- WBC (Platelets)
- Blood Platelet
- Plasma
- RBCs are biconcave and disc-like, while WBCs have an irregular amoeboid shape.
RBCs are smaller in size and devoid of nuclei. Meanwhile, WBCs are larger and have a nucleus. - Functions of:
- RBCs (erythrocytes): It contains haemoglobin pigment, which helps transport oxygen.
- WBC (Platelets): WBCs protect the body against infections, thus making them called soldiers of the body.
- Blood Platelet: Blood platelets are the initiators of blood clotting.
- The average life of RBC is about 120 days.
- Fibrinogen.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given below is certain structure, write the term for the functional activity.
Bone marrow and ………………………………..
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to phrase in bracket:
serum and vaccine (Composition)
Is it possible for the blood to clot under the skin? Give reason in support of your answer.
Name the following:
The phase of the cardiac cycle in which the ventricles get filled with blood from the atrium.
The blood vessel that begins and ends in capillaries is the ______.
Choose the correct answer:
Exchange of material between blood and interstitial fluid occurs only at the ________
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
R.B.Cs are of several kinds whereas WBCs are of one kind.
State the Function: R.B.C.
Choose the Odd One Out:
