Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given below is the representation of amino acid composition not the relevant translated portion of β-chain of haemoglobin, related to the shape of human red blood cells
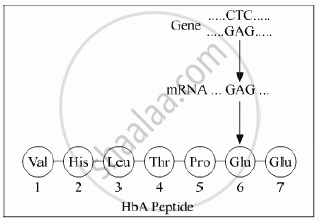
(a) Is this representation indicating a normal human or a sufferer from certain related genetic disease? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) What difference would be noticed in the phenotype of the normal and the sufferer related to this gene?
(c) Who are likely to suffer more from the defect related to the gene represented the males, the females or both males and females equally? And why?
उत्तर
(a) This representation is of a normal person. In a normal person the mRNA contains the codon GAG which codes for glutamic acid.
(b) In a sufferer, the codon GAG is replaced by GUG in the mRNA. Hence, during translation of the defective mRNA, Glutamic acid is replaced by Valine.
(c) The disease represented by the defect in the given gene is sickle-cell anaemia. It is an autosomal recessive trait. This disease is transmitted to the progeny when both the parents are carriers for the disease (heterozygous).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(a) Why are thalassemia and haemophilia categorized as Mendelian disorders? Write the symptoms of these diseases. Explain their pattern of inheritance in humans.
(b) Write the genotypes of the normal parents producing a haemophilic son.
Answer the following question.
Both Haemophilia and Thalessemia are blood-related disorders in humans. Write their causes and the difference between the two. Name the category of genetic disorder they both come under.
Webbed neck is characteristic of ______ syndrome.
Write a note on Down’s syndrome.
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
i. Genetic disorders are broadly categorised as, Mendelian disorders and chromosomal disorders.
ii. Mendelian disorders are caused due to absence or excess of one or more chromosomes or their abnormal arrangement.
iii. Chromosomal disorders are mainly caused due to alteration or mutation in the gene.
Identify the characteristics that are observed in an individual suffering from Klinefelter syndrome.
i. Gynaecomastia, under developed testis and no spermatogenesis.
ii. Voice pitch is harsh.
iii. They are tall with long arms.
If a genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only some of the male progeny, the disease is ______.
In sickle-cell anaemia, shape of RBCs under oxygen tension becomes ______.
Select the incorrect statement regarding pedigree analysis.
Klinefelters’ syndrome is characterised by a karyotype of ______.
