Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How is amplitude modulation achieved?
उत्तर
Amplitude modulation is the process of varying the amplitude of the carrier signal in accordance with the amplitude of the message signal.
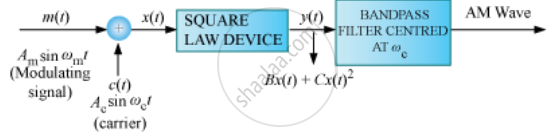
Amplitude modulated signals can be produced by adding the carrier signal with the message signal and passing the resultant signal through a square law device (eg: FET). Then the signal from the square law device is passed through band pass filter to allow only the signals centered at carrier frequencies to pass. The output of the band pass filter is power amplified and transmitted by the antenna.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain any two factors that justify the need of modulating a low-frequency signal.
Draw a block diagram of a detector for AM signal and show, using necessary processes and the waveforms, how the original message signal is detected from the input AM wave.
Explain the process of amplitude modulation.
The frequencies of two side bands in an AM wave are 640 kHz and 660 kHz respectively. Find the frequencies of carrier and modulating signal. What is the bandwidth required for amplitude modulation?
Write two advantages of frequency modulation over amplitude modulation.
Why is frequency modulation preferred over amplitude modulation for transmission of music?
On radiating (sending out) an AM modulated signal, the total radiated power is due to energy carried by ωc, ωc – ωm and ωc + ωm. Suggest ways to minimise cost of radiation without compromising on information.
An amplitude-modulated wave is represented by Cm(t) = 10(1 + 0.2 cos 12560t) × sin (111 × 104t) volts. The modulating frequency in kHz will be ______.
The maximum and minimum voltage of an amplitude modulated signal are 60 V and 20 V respectively. The percentage modulation index will be ______.
The maximum amplitude for an amplitude modulated wave is found to be 12V while the minimum amplitude is found to be 3V. The modulation index is 0.6x where x is ______.
