Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How do non-green plants such as fungi and bacteria obtain their nourishment?
उत्तर
Non-green plants such as fungi and bacteria obtain their nourishment from decaying organic matter in their environment. This matter comes from dead animals and plants. Fungi and bacteria break down the organic matter to obtain the nourishment and they release carbon dioxide back in the atmosphere.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The diagram is set up to demonstrate an experiment. Pond weed was placed in five water-filled tubes. The experiment was set up as shown in the diagram. The tubes were then left for 24 hours. Write the correct answer out of the five available choices:
(i) In which tube would you except to find the plant with the least amount of starch?
(a ) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 (e ) 5
(ii) The tube in which most oxygen would be found is
(a ) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 (e ) 5
(iii) The tube in which least carbon dioxide would be found is
(a ) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 (e ) 5
(iv) The tube in which the plant would survive for the shortest length of time is
(a ) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 (e) 5

Mention one difference between the following on the basis of what is given in bracket.
Chlorophyll and chloroplast (part of plant cell)
Photosynthesis in green plants is directly and indirectly dependent on so many plant structures.
Explain briefly the role of the following structures in this process is Xylem tissue in the leaf veins
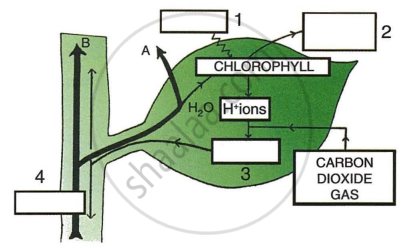
Given below is a schematic diagram to illustrate some aspects of photosynthesis.
- Fill up the gaps, in blank spaces (1-4), by writing the names of the correct items.
- What phenomenon do the thick arrows A and B indicate?
Given alongside is the diagram of an experimental set-up:

What alteration (s) will you make in it for obtaining expected result?
The diagram below shows two test-tubes A and B. Test-tube A contains a green water plant. Test-tube B contains both a green water plant and a snail. Both test-tubes are kept in sunlight. Answer the questions that follow:

(a) Name the physiological process that releases the bubbles of oxygen.
(b) Explain the physiological process as mentioned above in (a).
(c) What is the purpose of keeping a snail in test-tube B?
(d) Why does test-tube B have more bubbles of oxygen?
(e) Give an example of a water plant that can be used in the above experiment.
(f) Write the overall chemical equation for the above process.
Give technical term:
Name only one plant, you are familiar with which has no chlorophyll.
Give reasons/explain:
During the starch test, the leaf is boiled in water.
