Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How does change in the price of complementary good affect the demand for the given good? Explain with the help of an example.
उत्तर
Demand for a commodity in relation to the price of the complementary good
Complementary goods are purchased jointly such as ink and ink pens.
Increase in price of the complementary good:
If there is an increase in the price of a good, then the demand for another good will decline. So the demand curve shifts parallel to the left, i.e. from D1D1 to D2D2
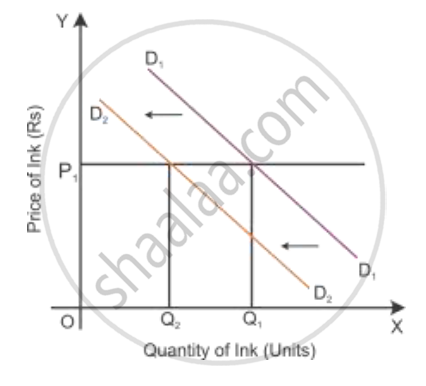
A decrease in the price of the complementary good:
If there is a decrease in the price of a good, then the demand for another good will increase. So the demand curve shifts parallel to the right, i.e. from D1D1 to D2D2.
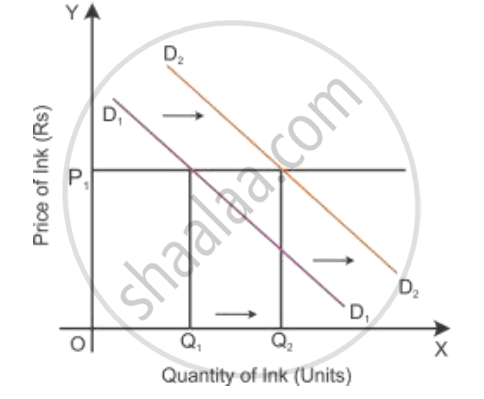
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain any two factors that affect the price elasticity of demand. Give suitable examples.
A 5 percent fall in the price of a good raises its demand from 300 units to 318 units. Calculate its price elasticity of demand.
State whether the following statement is true or false :
Concept of ‘elasticity of demand’ is useful for the finance minister.
Define or explain the following concepts (Any THREE):
Stock
Choose the correct answer :
Demand of electricity for domestic purpose is _________.
Elasticity of demand for two goods A and B is -2 and -3 respectively. Then good A has higher elasticity.
The government wants to reduce the consumption of good by 10%. The price elasticity of demand for elasticity is -0.4. The government should raise the price of elasticity by ______.
What is the implication of a vertical demand curve?
The price of Y falls from ₹ 8 to ₹ 6. The quantity demanded increases from 100 units to 125 units. The price electricity of demand will be ______.
When the price elasticity of demand for a good equals ______.
Which of the following is the most likely reason for the relatively high elasticity of bottled water?
Assertion (A): The demand for soap, salt, matches etc. is highly elastic.
Reason (R): The demand for soap, salt, matches etc. is highly inelastic because the consumer spends a very small amount of expenditure in relation to his/her income.
Explain briefly the factors on which elasticity of demand depends.
When will the demand curve be parallel to x-axis?
Comment upon the shape of the demand curve, if Ed = 0.
Discuss any three/ four factors determining price elasticity of demand.
How does the nature of a commodity affect its price elasticity of demand?
How does the nature of a good affect its elasticity of demand?
