Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How does change in the price of a substitute good affect the demand of the given good? Explain with the help of an example.
उत्तर
Substitute goods are goods which can be purchased in place of each other. The demand for
a commodity is in relation to the price of its substitute good. Assume tea and coffee as two
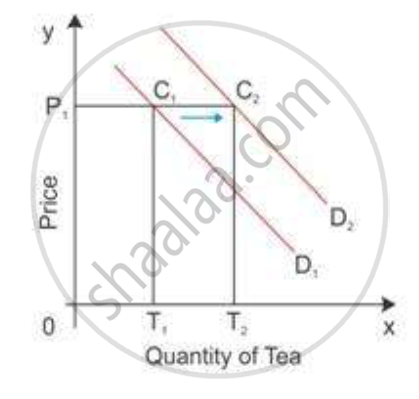
substitute goods. D1 is the demand curve for the demand for tea in the diagram.
When the price of tea is OP1, the quantity demanded is OT1 as shown in Fig (a). If there is an
increase in the price of the substitute good coffee, then the demand curve for tea shifts to
the right. Now, the consumer is willing to buy the P1C2 quantity of tea which is equal to OT2.
Greater the purchase of a commodity at its constant price points to a situation of increase
or forward shift in the demand curve. The consumer demand curve shifts from D1 to D2,
consuming more of tea even when its price is constant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State and explain the ‘law of demand’ with its exceptions.
When does ‘increase’ in demand take place?
Explain the effect of change in prices of the related goods on demand for the given good.
Distinguish between individuals demand and market demand.
Good Y is a substitute of good X. The price of Y falls. Explain the chain of effects of this change in the market of X.
Fill in the blank using proper alternative given in the bracket:
Market demand is a total demand of...............buyers.
Define or explain the following concept.
Market Demand .
State with reason, whether you Agree or Disagree with the following statement.
The demand curve slopes downward from left to right.
Write explanatory notes or answer the following.
Aggregate demand
Do you agree with the following statement? Give reason
There are no exceptions to the law of demand.
Do you agree with the following statement? Give reason
State and explain the law of demand.
Statements related to decrease in demand
- It is a type of change in demand
- It takes place due to unfavourable changes in other factors like tastes, income etc.
- Price remains constant
- Demand curve shifts to the right hand side of the original demand curve
Assertion (A): Under exceptional cases, demand curve has a positive slope.
Reasoning (R): In exceptional cases, consumer buys more when the price of a commodity rises and buys less when the price of commodity falls.
Assertion (A): The demand curve is downward sloping.
Reason (R): The income effect means with a fall in the price of a good, the consumer's real income or purchasing power rises and he demands more units of the good.
Study the following table and answer the questions:
| Price of Ice Cream (₹) | Quantity Supplied | Market Supply | ||
| Seller A | Seller B | Seller C | (A + B + C) | |
| 50 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 7 |
| 100 | 1 | `square` | 10 | 15 |
| 150 | `square` | 6 | 15 | 23 |
| 200 | 3 | 8 | 20 | `square` |
| 250 | 4 | 10 | `square` | 39 |
Questions:
- Complete the above table.
- State whether the following statements are True or False.
(a) Market supply has a direct relation to price.
(b) As the price rises from ₹50 to ₹250, market supply rises from 7 to 39. This indicates an increase in supply.
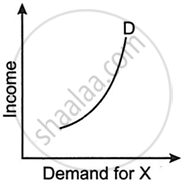
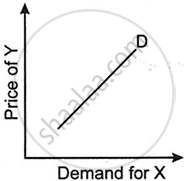
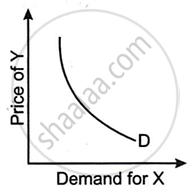
Figures (A), (B) and (C) given below represent different types of Demand curves.
 |
 |
 |
| (A) | (B) | (C) |
What kind of goods do each of these Demand curves represent? Give a reason for each of the curves.
Draw a straight-line demand curve joining both the axes. Indicate the following on the demand curve.
Elasticity of demand is equal to zero
