Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How price and output are determined under the perfect competition?
उत्तर
In the short run at least a few factors of production are fixed. The firms under perfect .competition take the price (10) from the industry and start adjusting their quantities produced.
For example
Qd = 100 -5P and
Qs = 5p
At equilibrium Qd = Qs
100 – 5p = 5p
100 = 5p + 5p
p = 10
Qd = 100 – 5(10)
= 50
Qs = 5(10) = 50
Qd = Qs
50 = 50

SS – market supply, DD – market demand, AR – Average Revenue, AC – Average Cost, MR – Marginal Revenue, MC – Marginal Cost This diagram consists of three panels.
- First part:
The equilibrium of an industry is explained. The demand and supply forces of the firms interact and the price is fixed as Rs.10. The equilibrium of an industry is obtained at 50 units of output. - Second part:
AC curve is lower than the price line. Equilibrium is achieved where
MC = MR. Equilibrium quantity is 50. With price Rs. 10, it experiences supernormal profit
AC = Rs. 8
AR = Rs. 10
TR – 50 x 10 = 500
TC = 50 x 8 = 400
Profit = 500-400= 100. - Third part:
The firm’s cost curve is above the price line. Equilibrium MC = MR. Quantity is 50 with price Rs. 10, it experiences loss (AC > AR)
TR = 50 x 10 = 500
TC = 50 x 12 = 600
Loss = 600-500= 100
If profit prevails in the market, new firms emerge results in declining prices and if loss occurs the existing loss-making firm exits results in increasing prices consequent upon the entry and exit of new firms into the industry, firms always earn ‘normal profit’ in the long run. - Price and output determination in long run:
The long-run equilibrium of the firm is illustrated in the diagram. Under perfect competition, long-run equilibrium is only at the minimum point of LAC. At point E,
LMC = MR = AR = LAC
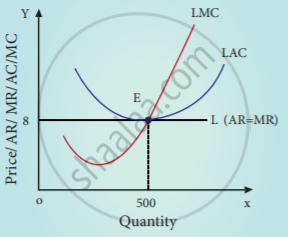
In the diagram AR = AC. Equilibrium is at point E where the price is 8 and output is 500. At this point, the profit of the firm is only normal. Thus condition for long-run equilibrium of the firm is Price = AR = MR = Minimum AC
At equilibrium SAC > LAC. Hence in the long-run equilibrium price is lower and quantity is larger compared to the short-run equilibrium price and quantity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Equilibrium condition of a firm is ______.
There is no excess capacity under ______.
In monopoly, MR curve lies below ______.
The average revenue curve under monopolistic competition will be ______.
Under perfect competition, the shape of demand curve of a firm is ______.
Draw demand curve of a firm for the following:
Perfect Competition
Specify the nature of entry of competitors in perfect competition and monopoly.
Mention the similarities between perfect competition and monopolistic competition.
Bring out the features of perfect competition.
Homogeneous product is a feature of this market.
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Perfect competition
- Oligopoly
Homogeneous product is a feature of this market.
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Perfect competition
- Oligopoly
Homogeneous product is a feature of this market.
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Perfect competition
- Oligopoly
