Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How solid waste management is carried out by composting?
उत्तर
- Composting is one of the important method for Solid Waste Management.
- Composting is a process by which organic matter is decomposed by microorganisms into nutrient rich, stable humus material called compost.
- Compost is peaty humus, dark in colour and has a crumbly texture, an earthy odour, and resembles rich topsoil.
- The composting process is an environmentally sound and beneficial means of recycling organic materials and not a means of waste disposal.
- It involves four main components: organic matter, moisture, oxygen, and microorganisms.
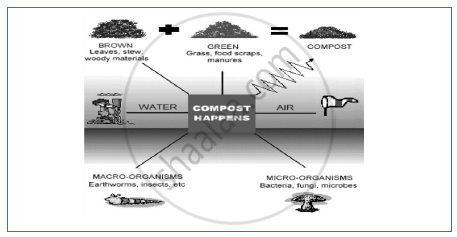
1. Organic matter includes crop residues, food garbage, animal wastes, some municipal wastes and suitable industrial wastes. Organic materials used for compost should include a mixture of brown organic material (dead leaves, twigs) and green organic material (lawn clippings, fruit rinds, vegetable peel etc.). Brown materials supply carbon, while green materials supply nitrogen. The best ratio is 1 part green to 1 part brown material.]
2. Shredding, chopping or mowing these materials into smaller pieces will help speed the composting process by increasing the surface area. The organic material is then blended together and piled up or put in special pits for composting.
3. Microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes (fungi-like bacteria) carry out the composting process. The first stage of the composting is the consumption of easily available sugars by bacteria, which causes a fast rise in temperature. The second stage involves bacteria and actinomycetes that cause cellulose breakdown. The last stage is concerned with the breakdown of the tougher lignins by fungi.
Microorganisms in the compost digest C as an energy source and ingest N as a protein source. The C: N proportion should be approximately 30 parts C to 1 part N by weight.
4. Temperatures between 30-60°C indicate rapid composting. Temperatures greater than 60°C reduce the activity of most organisms.
5. Aeration replaces oxygen-deficient air in the center of the compost pile with fresh air. Rapid aerobic decomposition occurs only when there is enough oxygen present. Regular mixing or turning of the pile fluffs up the material and increases air movement, enhances aeration and decreases compaction.
6. Moisture is needed for bacterial decomposition. A moisture content of 40-60 percent provides adequate moisture without limiting aeration.
