Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How will you verify the laws of refraction or how the refractive index of glass is determined in the laboratory?
उत्तर
Place a white sheet of paper on a drawing board. Put a rectangular slab of glass on this white sheet and trace out its boundary ABCD. At any point R on the edge AB, draw a normal NN’. Draw an incident ray PR at any angle say 30°. Fix two pins P1 and P2 vertically on the line PR and at a distance not less than 3 cm from each other. Looking through the other side of the block, fix two pins, P3 and P4 vertically on the white sheet, such that all the four pins P1, P2, P3, and P4 appear to be in a straight line as seen through the glass block. Mark the pinpoints with a fine pencil, remove the block and join the points P3 and P4 by the straight line RS.

PR represents the incident ray and RS represents the refracted ray. ∠PRN and ∠KRN’ are respectively angles of incidence and refraction.
With R as centre and convenient radius, draw a circle cutting the incident ray at Q and the refracted ray at Q’.
From Q and Q’, draw perpendiculars QT and QT’ on the normal NN’
Now sin i = `"QT"/"QR"`
and Sin r = `"Q’T’"/"Q’T’"`
μ = `Sin"i"/Sin"r"="QT"/"QR"."Q’R"/"Q’T’"="QT"/"Q’T’"`
Since QR = Q’R being the radius of the same circle.
Repeat this experiment for other angles of incidence, say 45° and 60°, and find μ.
It is found that for different values of i the ratio.
`sin"i"/Sin"r"` = constant
Thus, it is verified that,
(i) `sin"i"/Sin"r"` is a constant and is equal to aμg.
(ii) The incident the refracted ray and normal line in the same plane.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write a relationship between the angle of incidence and angle of refractions for a given pair of media
How must light travel out of a substance if it is not going to be refracted?
Draw diagrams to show the refraction of light from glass to air. In diagram, label the incident ray, refracted ray, the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r).
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) What is the line XX' called?
(iii) Complete the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray either meets XX' at a point or appears to come from a point on XX'. Label it as F, What is this point called?
Using the curve, how do you infer that for given prism, the angle of minimum deviation δmin is unique for the given light?
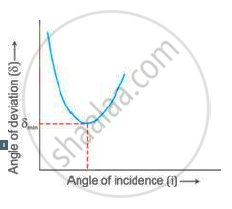
State the factors on which the angle of deviation depends.
Explain briefly what causes the twinkling of stars at night.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What should be the rate of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
The speed of light in air is 3 × 108 ms-1. Calculate the speed of light in water. The refractive index of water is 4/3.
A coin placed at the bottom of a beaker appears to be raised by 4.0 cm. If the refractive index of water is 4/3, find the depth of the water in the beaker.
