Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If one zero of the quadratic polynomial `kx^2 + 3x + k is 2`, then find the value of k.
उत्तर
Given: x = 2 is one zero of the quadratic polynomial `kx^2 + 3x + k`
Therefore, it will satisfy the above polynomial.
Now, we have
`k(2)^2 + 3(2) + k = 0`
⇒ 4k + 6 + k = 0
⇒ 5k + 6 = 0
⇒ k=`-6/5`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The graphs of y = p(x) are given in following figure, for some polynomials p(x). Find the number of zeroes of p(x).
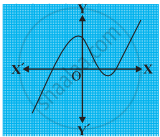
Write the zeros of the polynomial `f(x) = x^2 – x – 6`.
If ∝ and β are the zeros of the polynomial f(x) = `6x^2 + x - 2 `find the value of `(∝/β+∝/β) `
If one zero of the quadratic polynomial x2 + 3x + k is 2, then the value of k is ______.
Given that one of the zeroes of the cubic polynomial ax3 + bx2 + cx + d is zero, the product of the other two zeroes is ______.
If one of the zeroes of a quadratic polynomial of the form x² + ax + b is the negative of the other, then it ______.
If x3 + 1 is divided by x2 + 5, then the possible degree of quotient is ______.
If one of the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial (k -1)x² + kx + 1 the value of k is ______.
If f(x) = 5x - 10 is divided by x – `sqrt2`, then the remainder will be ______.
The zeroes of the quadratic polynomial 16x2 – 9 are ______.
