Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Illustrate a glycosidic, peptide and a phospho-diester bond.
उत्तर
1) Glycosidic bond is the type of chemical linkage between the monosaccharide units of disaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides, which is formed by the removal of a molecule of water.

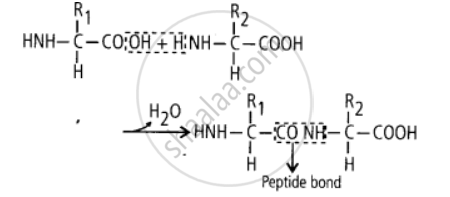
2) Peptide bonds are formed by the reaction between carboxyl (- COOH) of one amino acid and amino (- NH2) group of other amino acid with the elimination of water.
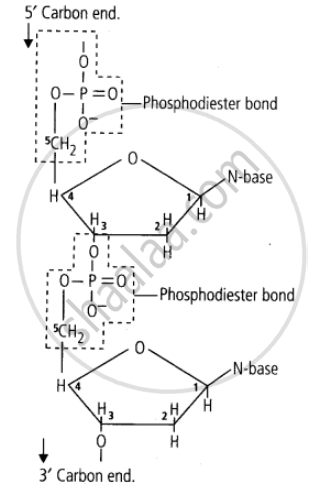
3) In a polynucleotide chain, adjacent nucleotides are joined together by a bond called phosphodiester bond. This bond links a phosphate group and sugar group of two adjacent nucleotides by means of an oxygen bridge.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Identify the substances having glycosidic bond and peptide bond, respectively in their structure:
Number of hydrogen bonds formed between guanine and cytosine is:
A unit composed of sugar and nitrogen base linked by glycosidic bond is ______.
Ester linkages occur in ______.
Select an appropriate chemical bond among ester bond, glycosidic bond, peptide bond and hydrogen bond and write against the following.
Polysaccharide ______
Select an appropriate chemical bond among ester bond, glycosidic bond, peptide bond and hydrogen bond and write against the following.
Fat ______
Select an appropriate chemical bond among ester bond, glycosidic bond, peptide bond and hydrogen bond and write against the following.
Water ______
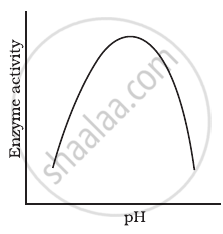
Enzymes are proteins. Proteins are long chains of aminoacids linked to each other by peptide bonds. Aminoacids have many functional groups in their structure. These functional groups are, many of them at least, ionisable. As they are weak acids and bases in chemical nature, this ionization is influenced by pH of the solution. For many enzymes, activity is influenced by surrounding pH. This is depicted in the curve below, explain briefly.
Nucleic acids exhibit secondary structure, justify with example.
Nucleic acids exhibit secondary structure. Describe through Wetson- Crick Model.
