Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Illustrate price and output determination under Monopoly.
उत्तर
Monopoly is a market structure characterized by a single seller, selling the unique product with the restriction for a new firm to enter the market.
Price and Output Determination under Monopoly:
Nature of cost and revenue curves:
A monopoly is a one-firm industry. Therefore, a monopolist firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve. Since AR falls, MR lies below the AR curve (MR < AR)
The monopolist will continue to sell his product as long as his MR > MC
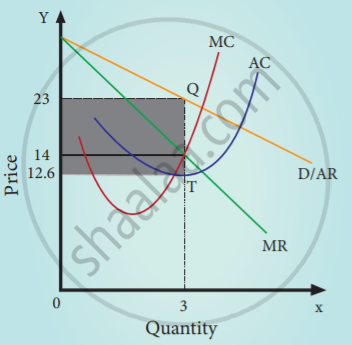
Condition for equilibrium:
Monopolists attain equilibrium at the level of output when MC = MR.
From the diagram, till he sells 3 units output, MR is greater than MC, and when he exceeds this output level, MR is less than MC. At equilibrium where MR = MC, price (AR) is Rs. 88. To know the profit of monopolists at equilibrium output, the average revenue curves and the average cost curves are used at equilibrium Output 3
AR= 88
AC = 50
Profit per unit = 88-50
= 38
= (AR – AC) × Total output
= (88 – 50) × 3
= 38 × 3
= 114
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A firm under monopoly can earn ______ in the short run.
Another name of price is ______.
Perfect competition assumes ______.
Price discrimination will always lead to
In which market form, does absence of competition prevail?
Who is price-taker?
Point out the essential features of pure competition.
Draw demand curve of a firm for the following:
Monopoly
Mention any two types of price discrimination.
Define “Excess capacity”.
Describe the degrees of price discrimination.
