Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Illustrate the law of conservation of energy by discussing the energy changes which occur when we draw a pendulum bob to one side and allow it to oscillate. Why does the bob eventually come to rest? What happens to its energy eventually? Is it a violation of the law of conservation of energy?
थोडक्यात उत्तर
उत्तर
- A basic pendulum is a little metallic ball (known as a bob) suspended by a light string (thread) from a frictionless, solid support. A simple pendulum is depicted in the illustration.
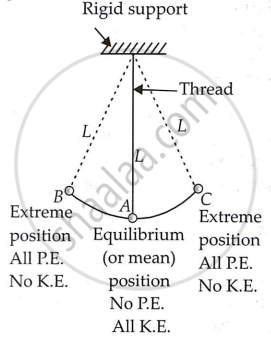
- A basic pendulum swings from extreme positions to its mean position.
- The bob is at its highest position at the extreme positions and at its lowest at its mean position.
- The graphic depicts the energy changes that occur when the bob is in motion. So, when a pendulum swings back and forth, its energy changes in the following order.
Extreme right position-All P.E., No K.E. ↓ Mean position-No P.E. All K.E. ↓ Extreme left position-All P.E., No K.E. ↓ Mean position-No P.E. All K.E. ↓ I Extreme right position-All P.E., No K.E.
shaalaa.com
या प्रश्नात किंवा उत्तरात काही त्रुटी आहे का?
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State and explain the law of conservation of energy with an example.
Explain how, the total energy a swinging pendulum at any instant of time remains conserved. Illustrate your answer with the help of a labelled diagram.
The following data was obtained for a body of mass 1 kg dropped from a height of 5 metres :
|
Distance above ground |
Velocity |
| 5 m | 0 m/s |
| 3.2 m | 6 m/s |
| 0 m | 10 m/s |
Show by calculations that the above data verifies the law of conservation of energy (Neglect air resistance). (g = 10 m/s2).
