Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Illustrate the Ricardian Theory of Rent.
दीर्घउत्तर
उत्तर
The classical theory of rent is called “Ricardian theory of rent”.
- Definition:
Rent is that portion of the produce of the earth which is paid to the landlord for the use of the original and indestructible powers of the soil. - Assumptions:
- Land differs infertility.
- The law of diminishing returns operates in agriculture.
- Rent depends upon the fertility and location of the land.
- The theory assumes perfect competition and a long period.
- There is the existence of marginal land or no-rent land.
- The land has certain “Original and indestructible powers”.
- The land is used for cultivation only.
- Most fertile lands are cultivated first.
- Statement of the theory with illustration:
Assume that some people settle in the newly discovered islands. People will first cultivate the most fertile ‘A’ grade land. They produce 40 bags of paddy.
Suppose after some time if another group of people settles down on the same island. They cultivate ‘B’ grade land which produces 30 bags of paddy. Suppose yet another group of people settle down there they cultivate ‘C’ grade land. It produces 20 bags of paddy.
This surplus of ‘A’ grade land is now raised to 20 bags (40 – 20) and it is the ‘Economic Rent’ of ‘A’ grade land. The surplus of ‘B’ grade land is 10 bags (30 – 20). In ‘C’ grade land cost of production is equal to the price of its products and it does not yield any rent (20 – 20). Hence ‘C’ grade land is called ‘no-rent land’ or marginal land.
The land which yields rent is called “intra-marginal land”.
Rent indicates the differential advantage of the superior land over the marginal land. - Ricardian Theory of Rent:
| Grades of Lands | Production (in bags) | Surplus (i.e., Rent in bags) |
| A | 40 | 40-20=20 |
| B | 30 | 30-20= 10 |
| C | 20 | 20-20= 0 |
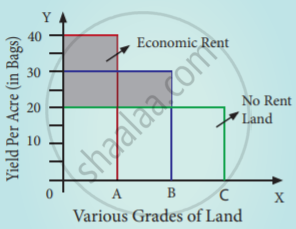
- Diagrammatic illustration:
The X-axis represents various grades of land and the Y-axis yield per acre (in bags). OA, AB, and BC are the ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’ grade lands respectively.
The ‘C’ grade land is the no-rent land. A and B grade lands are “intra-marginal lands. The economic rent yielded by ‘A’ and ‘B’ grade lands is equal to the shaded area of their respective rectangles. - Criticisms:
- The order of cultivation from most fertile to least fertile lands is historically wrong.
- This theory assumes that rent does not enter into price. But in reality, rent enters into the price.
shaalaa.com
Rent
या प्रश्नात किंवा उत्तरात काही त्रुटी आहे का?
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Rent is the reward for the use of
The concept of ‘Quasi-Rent’ is associated with
The Classical Theory of Rent was propounded by
‘Original and indestructible powers of the soil’ is the term used by
Quasi-rent arises in
Define ‘Rent’.
What are the motives of demand for money?
Distinguish between rent and quasi-rent.
