Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a fertilised embryo sac, the haploid, diploid, and triploid structures are ______.
पर्याय
Synergid, zygote, and primary endosperm nucleus
Synergid, antipodal and polar nuclei
Antipodal, synergid, and primary endosperm nucleus
Synergid, polar nuclei and zygote
उत्तर
In a fertilised embryo sac, the haploid, diploid, and triploid structures are synergid, zygote, and primary endosperm nucleus.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
'Formation of primary endosperm nucleus is called triple fusion'. Give reason
(a) Explain the events after pollination leading to the formation of a seed in angiosperms.
(b) Mention the ploidy levels of the cells of different parts of an albuminous seed.
During double fertilization second male gamete fuses with ___________.
What happens to the following after fertilization?
Stamens
Given ahead is a diagrammatic sketch of the sectional view of a germinating pollen grain. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
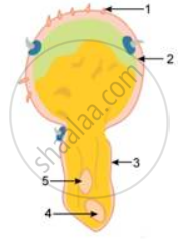
Where does the germination of the pollen grain take place and how?
Given ahead is a diagrammatic representation of the process of fertilization. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
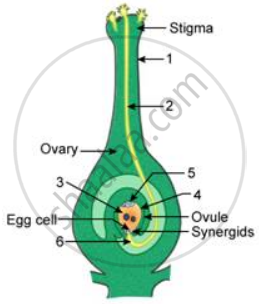
Name the parts labelled 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6.
Explain the pollination process in Salvia
Explain the pollination process in maize.
Define fertilization.
What is the function of pollen tube? Explain with the help of a diagram.
Describe the process of double fertilization.
Male gametes in angiosperms are formed by the division of ______.
What is Mellitophily?
In double fertilization, the first male gamete fuses with the egg and the second male gan1ete fuses with which of the following?
From the following identify the fate of the male gametes discharged in the synergid.
Double fertilisation was first discovered in 1898 by ______ in Fritillaria and Lilium.
After fertilization, the seed coat of seeds develops from ______
Name the part of gynoecium that determines the compatible nature of pollen.
