Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
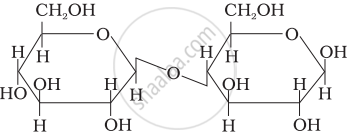
In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e. aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars. Which of the following disaccharide is a non-reducing sugar?
पर्याय
उत्तर

Explanation:
This structure represents sucrose in which α-D glucose and β-D-fructose is attached to each other by C1 – C2 glycosidic linkage.
Since, reducing groups of glucose and fructose are involved in glycosidic bond formation, this is considered as non-reducing sugar.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent?
HNO3
The sugar that is characteristic of milk is ____________.
Which one is a disaccharide?
Sucrose on hydrolysis gives:
Which one of the following statement is correct about sucrose?
Match the following enzyms given in Column I with the reactions they catalyse given in Column II.
| Column I (Enzymes) | Column II (Reactions) |
| (i) Invertase | (a) Decomposition of urea into NH3 and CO2 |
| (ii) Maltase | (b) Conversion of glucose into ethyl alcohol |
| (iii) Pepsin | (c) Hydrolysis of maltose into glucose |
| (iv) Urease | (d) Hydrolysis of cane sugar |
| (v) Zymase | (e) Hydrolysis of proteins into peptides |
Maltose is made of
Which disaccharide is present in milk?
Which of the following is a reducing sugar?
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called ______.