Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In figure give below of thin concave lens, F1 and F2 are its foci, complete the path of the given ray of light after it emerges out of the lens.
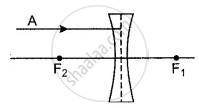
उत्तर
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
List some things that concave lens and concave mirror have in common.
An object 2 cm tall stands on the principal axis of a converging lens of focal length 8 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image formed if the object is:
(i) 12 cm from the lens
(ii) 6 cm from the lens
State one practical application each of the use of such a lens with the object in position (i) and (ii).
Which type of lens is :
a converging lens, and which is
When sunlight is concentrated on a piece of paper by a spherical mirror or lens, then a hole can be burnt in it. For doing this, the paper must be placed at he focus of:
(a) either a convex mirror or convex lens
(b) either a concave mirror or concave lens
(c) either a concave mirror or convex lens
(d) either a convex mirror or concave lens
When an object is placed 10 cm in front of lens A, the image is real, inverted, magnified and formed at a great distance. When the same object is placed 10 cm in front of lens B, the image formed is real, inverted and same size as the object.
What is the nature of lens B?
When a fork is seen through lenses A and B one by one, it appears as shown in the diagrams. What is the nature of (i) lens A, and (ii) lens B? Give reason for your answer.
(a) Find the position and size of the virtual image formed when an object 2 cm tall is placed 20 cm from:
(i) a diverging lens of focal length 40 cm.
(ii) a converging lens of focal length 40 cm.
(b) Draw labelled ray diagrams to show the formation of images in case (i) and (ii) above (The diagrams may not be according to scale).
A person finds difficulty in seeing nearby objects clearly. His vision can be corrected by using spectacles containing:
(a) converging lenses
(b) diverging lenses
(c) prismatic lenses
(d) chromatic lenses
An object is placed on the axis of a lens. An image is formed by refraction in the lens. For all positions of the object on the axis of the lens, the positions of the image are always always between the lens and the object.State three characteristics of the image.
An object is placed at a distance of 60 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm.
(i) Use the lens formula to find the distance of the image from the lens.
(ii) List four characteristics of the image (nature, position, size, erect/inverted) formed by the lens in this case.
(iii) Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer of the part (ii).
