Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
4 tones of bauxite, 150 Kg of sodium hydroxide and 600 Kg of graphite.
The aluminium compound in bauxite is aluminium oxide and the main impurity is iron (II) oxide. Aluminium is obtained by the electrolysis of aluminium oxide dissolved in cryolite.
(a) When bauxite is treated with sodium hydroxide solution, what happens to:
(i) the aluminium oxide?
(ii) The iron (III) oxide?
उत्तर
(i) Aluminium oxide being an amphoteric oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide solution to form soluble sodium meta aluminate.
\[\ce{\underset{\text{Alumina}}{Al2O3.2H2O} + 2NaOH + 2H2O ->\underset{\text{Sodium aluminate}}{2NaAIO2} + 3H2O}\]
(ii) Iron (III) oxide remains undissolved in the sodium hydroxide solution and settles down.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the following:
A metal oxide that can be reduced by hydrogen.
How is the following metallic oxide reduced? Write equations:
Iron (ll) oxide
Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the following reactions :
(i) Reduction of copper (II) oxide by hydrogen
Give equation for the following conversion: Ferric oxide to iron.
Name a non-metallic element which has a metallic lustre
In order to obtain one tone of aluminium, the following inputs are required:
4 tones of bauxite, 150 Kg of sodium hydroxide and 600 Kg of graphite.
The aluminium compound in bauxite is aluminium oxide and the main impurity is iron (II) oxide. Aluminium is obtained by the electrolysis of aluminium oxide dissolved in cryolite.
(i) Write the formula of cryolite.
(ii) Write down the word which correctly completes the following sentence.
"By dissolving aluminium oxide in cryolite, a ______ (conducting / non- conducting) solution is produced.
(iii) Why so much graphite required for this electrolytic process.
(iv) Write the equation for the reaction which takes place at cathode.
Complete the following by selecting the correct option from the choices given :
The metal whose oxide, which is amphoteric, is reduced to metal by carbon reduction ________
Name two metallic oxides which cannot be reduced by carbon, carbon monoxide or hydrogen.
Give the equation for the reduction of Iron (III) oxide.
The following sketch represents the electroplating of an Iron cup with Nickel metal.
Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
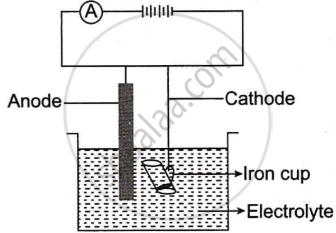
- During electroplating, the iron cup is placed at the cathode. Why?
- Name the ion that must be present in the electrolyte.
- State one condition that is necessary to ensure that the deposit is smooth, firm and even.
- Write the reaction taking place at the cathode.
- What change would you observe at the anode?
