Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the embryos of a typical dicot and a grass, true homologous structures are ______.
पर्याय
Coleorhiza and coleoptile
Coleoptile and scutellum
Cotyledons and scutellum
Hypocotyl and radicle
उत्तर
In the embryos of a typical dicot and a grass, true homologous structures are cotyledons and scutellum.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the development of dicot embryo.
From the following identify the non endospermic seeds.
The first cell of the suspensor towards the micropylar end becomes swollen and function as a ______.
During embryo development, the embryonal initial cell undergoes a transverse and two vertical divisions at right angles to each other to form ______.
In the young cob of maize, numerous filamentous hair like structures protruding from its tip are ______.
The arrangement of the nuclei in a normal embryo sac in the dicot plants is ______.
Vivipary automatically limits the number of offsprings in a litter. How?
In the given diagram, write the names of parts shown with lines.
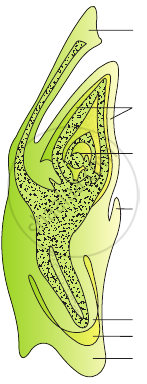
Starting with the zygote, draw the diagrams of the different stages of embryo development in a dicot.
Match column I with Column II. The fate of various parts of the ovary.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Ovary wall | (i) Testa |
| B. Outer integument | (ii) Stalk of the seed |
| C. Nucellus | (iii) Pericarp |
| D. Funicle | (iv) Perisperm |
Choose the correct code given below.
