Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Lipoprotein lipase deficiency (LPLD)is a genetic disorder in which a person has a defective gene for lipase. This leads to high triglycerides, stomach pain, and fat deposits under the skin. It may eventually affect the liver, pancreas and may also cause diabetes. The disorder occurs if a child acquires defective genes from both parents (autosomal recessive). ERT (enzyme replacement treatment) is one of the treatments offered to patients with LPLD.
-
- What procedure is followed in ERT?
- What could be one possible drawback of ERT?
- How can LPLD be treated using Biotechnology? Elaborate.
उत्तर
-
- Functional enzyme lipase is given to the patient by injection.
- This procedure is not completely curative.
-
- The disease can be treated by using Gene therapy.
- Gene therapy is a collection of methods that allows the correction of a gene defect that has been diagnosed in a child/embryo.
- Here, genes are inserted into a person’s cells and tissues to treat a disease. Correction of a genetic defect involves the delivery of a normal gene into the individual or embryo to take over the function of and compensate for the non-functional gene.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why are color-blindness and thalassaemia categorised as Mendelian disorders? Write the symptoms of these diseases seen in people suffering from them.
Match the column-I with column-II and re-write the matching pairs.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| 1. 21 trisomy | a. Turner’s syndrome |
| 2. X-monosomy | b. Klinefelter’s syndrome |
| 3. Holandric traits | c. Down's syndrome |
| 4. Feminized male | d. Hypertrichosis |
Thalassemia and sickle cell anaemia are caused due to a problem in globin molecule synthesis. Identify the correct statement from the following.
Thalassemia and sickle cell anemia are caused due to a problem in globin molecule synthesis. Select the correct statement.
Mongolism is a genetic disorder which is caused by the presence of an extra chromosome number ______.
Klinefelters’ syndrome is characterised by a karyotype of ______.
Read the following and answer from given below:
Turner's syndrome is an example of monosomy. It is formed by the union of an allosome-free egg and a normal 'X' containing sperm or a normal egg and an allosome-free sperm. The individual has 2n = 45 chromosomes (44 + X0) instead of 46. Such individuals are sterile females who have rudimentary ovaries, underdeveloped breasts, small uterus, short stature, webbed neck, and abnormal intelligence. They may not menstruate or ovulate. This disorder can be treated by giving female sex hormones to women from the age of puberty to make them develop breasts and have menstruation. This makes them feel more normal.
Which of the following statements regarding Turner's syndrome is incorrect?
Which of the following is called as Royal disease?
Fused ear lobes appear in the progeny due to an autosomal recessive gene. Work out the genotypes of number in the given pedigree.
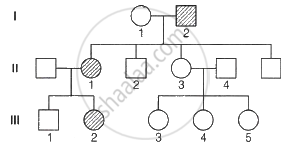
Describe Klinefelter’s syndrome.
