Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Make a punnett square for finding out the proportion of different genotypes in the progeny of a genetic cross between.
A pure tall (TT) pea plant with a pure dwarf (tt) pea plant.
उत्तर
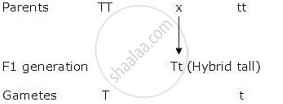
F2 generation
| Gametes | T | t |
| T | TT | Tt |
| t | Tt | tt |
Genotype - 1(Homozygous tall) :2 (Heterozygous tall):1 (Homozygous dwarf)
Phenotype - 3 (Tall) :1(Dwarf)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Appearance of new combinations in F2 generation in a dihybrid cross proves the law of_____________ .
- dominance
- segregation
- independent assortment
- purity of gametes
In Mendel’s experiments, tall pea plants (T) are dominant over dwarf pea plants (t).
What is a Dihybrid Cross?
In heterozygous condition, both the alleles are expressed in ______
A heterozygous violet-flowered pea plant is crossed to another homozygous violet- flowered pea plant. What percent of the progeny plants will have the recessive trait, i.e., white flowers?
Which is the one characteristic of the parents that can be inherited by their children?
Give reasons for the appearance of new combinations of characters in the F2 progeny.
How many pairs of contrasting characters in pea bad were chosen by Mendel?
In order to obtain the F1 generation Mendel pollinated a pure-breeding tall plant with a pure breeding dwarf plant. But for getting the F2 generation, he simply self-pollinated the tall F1 plants. Why?
Which one of the following cannot be explained on the basis of Mendel’s Law of Dominance?
Purity of gametes is linked to ______.
