Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Male and female gametes are __________.
पर्याय
diploid
haploid
उत्तर
Male and female gametes are haploid.
Explanation:
This means they have half as many chromosomes as diploid cells. During fertilisation, haploid gametes from both parents combine to form a diploid zygote with a full complement of chromosomes.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give the name and function for ‘A’ and ‘B’ from the diagram given below
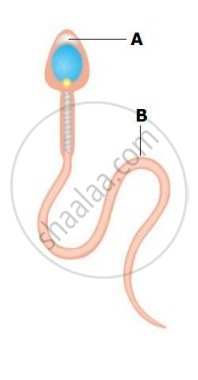
Draw a diagram of the microscopic structure of human sperm. Label the following parts in it and write their functions
(a) Acrosome
(b) Nucleus
(c) Middle piece
Mammalian egg is ____________.
Draw a labeled sketch of a spermatozoan.
Formation of ____________ is an indication of the termination of oogenesis.
Which of the following is diploid?
______ undergoes 2nd meiotic division during spermatogenesis.
By which process sperms released from the seminiferous tubules?
How many functional sperms and how many ova will be formed by a primary spermatocyte and a primary oocyte.
In spermatogenesis, reduction division of chromosome occurs during conversion of ______.
1st polar body is formed at which stage of oogenesis?
The prostate gland and seminal vehicle perform the function of ______.
Select the correct sequence of stages of spermatogenesis in a human male ______.
After the release of the secondary oocyte, the Graafian follicle develops into ______.
Mark the odd one.
Read the following and answer from given below:
Oogenesis is the process of the formation of an ovum in the ovaries. It consists of three phases: multiplication, growth, and maturation. Oogenesis is controlled by hormones GnRH, LH, FSH. GnRH secreted by the hypothalamus stimulates the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland to secrete LH and FSH.
Which cell division is involved in the formation of secondary oocytes?
What does figure represent?

Meiotic division of the secondary oocyte completed ______.
The diagram given below shows the various steps in spermatogenesis.
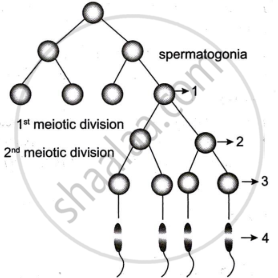
- Name the parts labelled '1', '2' and '3'.
- Name the process by which part '3' changes to part '4'.
Draw a labelled diagram of a section through ovary.
