Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match the column (A) with the column (B)
| (A) | (B) | ||
| (a) | Parenchyma | (i) | Thin walled, packing cells |
| (b) | Photosynthesis | (ii) | Carbon fixation |
| (c) | Aerenchyma | (iii) | Localized thickenings |
| (d) | Collenchyma | (iv) | Buoyancy |
| (e) | Permanent tissue | (v) | Sclerenchyma |
जोड्या लावा/जोड्या जुळवा
उत्तर
| (A) | (B) | ||
| (a) | Parenchyma | (i) | Thin walled, packing cells |
| (b) | Photosynthesis | (ii) | Carbon fixation |
| (c) | Aerenchyma | (iv) | Buoyancy |
| (d) | Collenchyma | (iii) | Localized thickenings |
| (e) | Permanent tissue | (v) | Sclerenchyma |
shaalaa.com
या प्रश्नात किंवा उत्तरात काही त्रुटी आहे का?
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Draw a well labelled diagram of xylem.
Write a short note on sclerenchyma.
What is the differences between collenchyma and sclerenchyma?
Study the diagram given below and then answer the question that follows:
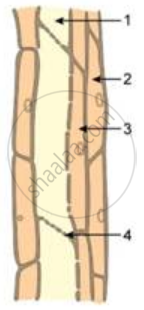
Where is this tissue likely to be found in the plant?
Give the structure and function of the following:
Crystal
The question has four answers. Choose the correct answer:
Phloem parenchyma, sclerenchyma, sieve tubes, and companion cells are found in
Name the two types of sclerenchyma cells.
Differentiate fibers from sclereids.
