Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match the items in column I with those in column II
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | Xylem | (i) | semi - permeable |
| (b) | Phloem | (ii) | permeable |
| (c) | Cell membrane | (iii) | downward flow of sap |
| (d) | Root pressure | (iv) | upward flow of water |
| (e) | Cell wall | (v) | guttation |
उत्तर
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | Xylem | (iv) | upward flow of water |
| (b) | Phloem | (iii) | downward flow of sap |
| (c) | Cell membrane | (i) | semi - permeable |
| (d) | Root pressure | (v) | guttation |
| (e) | Cell wall | (ii) | permeable |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the following:
The process by which water enters root hairs.
What part is played by The cytoplasm in the uptake of water into the root hair?
The diagram given below represents the results of an experiment conducted on two freshly taken leafy shoots of a herbaceous plant. The lower ends of the shoots dip in ordinary water.
(i) What is the aim of the experiment?
(ii) Some parts of the stem in both the shoots have been removed. Name the conducting tissue in shoot (a) and in shoot (b) that has been removed.
(iii) What are the results of this experiment?

The diagram below represents a layer of epidermal cells showing a fully grown root hair. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
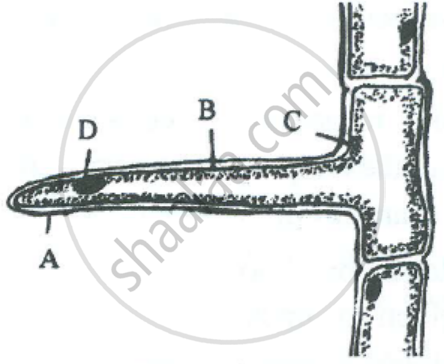
Mention one distinct difference between the parts labelled A and B.
Fill in the Blank
Leaves get wilted if _________ is removed from the plant.
Root hair is ________ extension of epiblema cells.
From which type of cells, root hair is originated
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the Root tip showing the root hair zone.
Give other name of epidermal cells in roots of plants.
