Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Name the following:
A potometer is an instrument for measuring the rate of the most transpiration in a herbaceous plant like Balsam occurs through which part.
उत्तर
Stomata
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the following:
Any two parts of a leaf which allow transpiration.
Choose the correct answer:
Stomata can open in night also in _______________
Differentiate Between Stomata and Hydathodes.
Given below is the diagram of an experimental set up to study the process of transpiration in plants. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:

(i) What is the colour of dry cobalt chloride paper?
(ii) Is the experimental leaf a monocot or a dicot? Give a reason to support your answer.
(iii) Why axe glass slides placed over the dry cobalt chloride papers?
(iv) After about half an hour what change, if any, would you expect to find in the cobalt chloride paper placed on the dorsal and ventral sides of the leaf? Give a reason to support your answer.
(v) Define the term ‘transpiration’.
The apparatus shown here is Girreau’s poto-meter designed to demonstrate unequal transpiration from the two surfaces of a dorsiventral leaf. Before keeping the leaf in between the cups, anhydrous calcium chloride (CaCl2) contained in two small vials were weighed and placed in both the cups. The ends of the cups were closed with corks through which two mercury manometers were connected. After a few hours, CaCl2 vials were taken out and weighed again.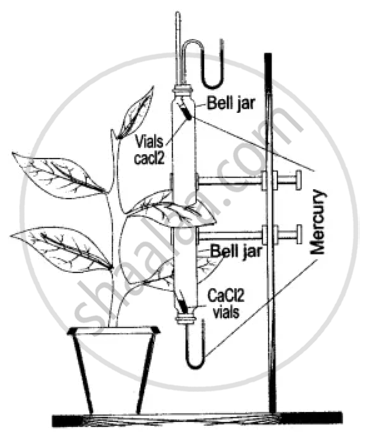
(i) What is the purpose of keeping CaCl2 vials inside the cup?
(ii) After a few hours, the CaCl2 vials were taken out and weighed again. Will you expect any difference in weight? If so, give reasons.
(iii) What was the purpose of using a mano-meter?
(iv) What do you mean by transpiration?
Name the following:
A plant having sunken stomata.
Mark the most appropriate answer in the following:
In the mechanism of opening and closing of stomata, the important factor is
How will you differentiate the different types of transpiration?
Write a short note on lenticular transpiration.
