Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
No chemical reaction takes place when granules of a rusty-brown solid A are mixed with the powder of another solid B. However, when the mixture is heated, a reaction takes place between its components. One of the products C is a metal and settles down in the molten state while the other product D floats over it. It was observed that the reaction is highly exothermic.
(a) What could the solids A and B be?
(b) What are the products C and D most likely to be?
(c) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between A and B leading to the formation of C and D. Mention the physical states of all the reactants and products in this equation and indicate the heat change which takes place.
(d) What is the special name of such a reaction? State one use of such a reaction.
(e) Name any two types of chemical reactions under which the above reaction can be classified.
उत्तर
(a) The rusty-brown solid A is iron (III) oxide and another solid B is aluminium. Mixing of iron granules with aluminium powder will have no reaction.
(b) The product are likely to be C (iron) and D (aluminium oxide). Once the mixture of iron (III) oxide granules and aluminium powder is heated, aluminium acts as reducing agent. Aluminium reduces iron (III) oxide to iron and aluminium powder oxidises to aluminium oxide with the liberation of excess heat.
(c) 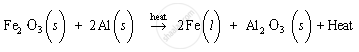
When A (iron (III) oxide) and B (aluminium powder) are heated, iron and aluminium oxide get produced with the liberation of excess heat. Thus, the product C is iron and product D is aluminium oxide. As excess heat is liberated in the reaction, the product C, i.e., iron metal, is in the molten state.
(d) The special name given to this reaction is thermite reaction. This reaction is widely used to weld broken hard substances like iron in railway tracks. This process of welding is called thermite welding.
(e) The above said reaction can be classified into displacement reaction and oxidation-reduction reaction. Aluminium, being more reactive than iron, displaces iron in iron (III) oxide, undergoing displacement reaction. Aluminium also acts as a reducing agent and reduces iron (III) oxide to iron metal and gets oxidised to aluminium oxide, undergoing oxidation-reduction reaction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two methods by which rusting of iron can be prevented are ______ and ______.
Explain why rusting of iron objects is faster in coastal areas than in deserts.
Explain why Iron sheets are coated with zinc during galvanization.
What is meant by galvanisation? Why is it done?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The corrosion of iron is called ................
What is corrosion?
Name any two metals which do not corrode easily.
Explain how the activity series accounts for each of the following:
tendency to corrosion
Corrosion can be an advantage in some case.Explain ?
Complete the process of iron rusting by filling the blanks. Suggest a way to prohibit the process.
The iron rust is formed due to........................... reaction. Different
regions on iron surface become anode and cathode.
Reaction on anode region :
`F_e(s) → Fe^(2+) (aq) +2e^-`
Reaction on anode region :
`O_2(g) + 4H^+(aq) +............................ → 2H_2 O (l) `
When Fe2+ ions migrate from anode region they react with ................... to form Fe3+ ions.
A reddish coloured hydrated oxide is formed from ............... ions. It is called rust.
`2Fe_(3+) (aq) + 4H_2O(l) → ................. + 6H_+(aq) `
A way to prevent rusting ..................................................................
What is "rusting"? Describe with a labelled diagram an activity to investigate the conditions under which iron rusts.
Give reason.
An iron article should be given a coat of paint
To prevent corrosion of iron and steel _______ method is used.
Stainless steel is an alloy of _______.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Write the name.
An alloy of copper and tin-
What is rust?
Identify the correct statement from the following:
Generally, when metals are treated with mineral acids, hydrogen gas is liberated but when metals (except Mn and Mg), treated with HNO3, hydrogen is not liberated, why?
Explain the following:
Lime water turns milky on passing carbon dioxide gas into it.
