Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Obtain the equation for resolving power of optical instrument
उत्तर
- For a single rectangular slit, the half-angle θ subtended by the spread of central maximum is given by the relation,
a sin θ = λ - Similar to a rectangular slit, when a circular aperture or opening forms an image of a point object, the image formed will not be a point but a diffraction pattern of concentric circles that become fainter while moving away from the centre. These are known as Airy’s discs. The circle of central maximum has the half angular spread given by the equation,
a sin θ = 1.22 λ - The numerical value 1.22 comes for central maximum formed by circular apertures.
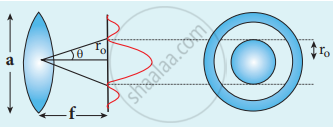
Airy’s discs
For small angles, sin θ ≈ θ
a θ =1.22 λ
Rewriting further,
θ = 1.22 λ/a and
`"r"_0/"f" = (1.22 lambda)/"a"`
`"r"_0 = (1.22lambda"f")/"a"` - This equation is called spacial resolution.
- When two-point sources close to each another form image on the screen, the diffraction pattern of one point source can overlap with another and produce a blurred image. To obtain a good image of the two sources, the two-point sources must be resolved i.e., the point sources must be imaged in such a way that their images are sufficiently far apart that their diffraction patterns do not overlap.
- According to Rayleigh’s criterion, for two-point objects to be just resolved, the minimum distance between their diffraction images must be in such a way that the central maximum of one coincides with the first minimum of the other and vice versa. Such an image is said to be just resolved image of the object. Rayleigh’s criterion is said to be the limit of resolution.
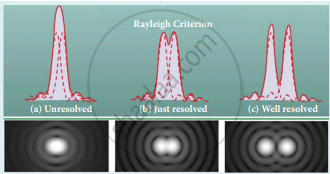
Rayleigh’s criterion - According to Rayleigh’s criterion the two-point sources are said to be just resolved when the distance between the two maxima is at least r0. The angular resolution has a unit in radian (rad) and it is given by the equation,
`theta = (1.22 lambda)/"a"` - The ability of an optical instrument to separate or distinguish small or closely adjacent objects through the image formation is said to be the resolving power of the instrument.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two coherent monochromatic light beams of intensities I and 4I are superposed. The maximum and minimum possible intensities in the resulting beam are ______.
First diffraction minimum due to a single slit of width 1.0 × 10-5 cm is at 30°. Then wavelength of light used is ______.
Differentiate between Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction.
Mention the differences between interference and diffraction.
Discuss the special cases on first minimum in Fraunhofer diffraction.
What is a diffraction grating?
What is resolution?
Discuss diffraction at single slit and obtain the condition for nth minimum.
Discuss the diffraction at a grating and obtain the condition for the mth maximum.
Discuss the experiment to determine the wavelength of monochromatic light using a diffraction grating.
Discuss the experiment to determine the wavelength of different colours using diffraction grating.
Light of wavelength of 5000 Å produces diffraction pattern of the single slit of width 2.5 μm. What is the maximum order of diffraction possible?
Consider sunlight incident on a slit of width 104 A. The image seen through the slit shall ______.
Consider sunlight incident on a pinhole of width 103A. The image of the pinhole seen on a screen shall be ______.
- a sharp white ring.
- different from a geometrical image.
- a diffused central spot, white in colour.
- diffused coloured region around a sharp central white spot.
