Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Sensory nerve of a reflex arc carries information from the receptor cells to the ______.
पर्याय
spinal cord
brain
muscles of the effector organ
bones of the receptor organ
उत्तर
Sensory nerve of a reflex arc carries information from the receptor cells to the spinal cord.
Explanation:
A reflex action, or reflex, is an automatic reaction to a stimulus that is not under conscious control. A reflex arc is a neural pathway that mediates a reflex action. The Central Nervous System (CNS), which is composed of the brain and spinal cord, receives data from the receptor cell via the sensory nerve of a reflex arc. The sensory nerve fibres in the body terminate in the spinal cord, where motor neurons that control the effector organ share synapses with interneurons to transmit information.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Reflex arc is formed by:
Assertion: Reflex Arc works faster than the thinking process of the brain.
Reason: Reflex Arc works in the case of those animals who do not have a thinking process.
Which of the following statements are true?
- Sudden action in response to something in the environment is called reflex action
- Sensory neurons carry signals from spinal cord to muscles
- Motor neurons carry signals from receptors to spinal cord
- The path through which signals are transmitted from a receptor to a muscle or a gland is called reflex arc
Label the parts (a), (b), (c) and (d) and show the direction of flow of electrical signals in the given figure.
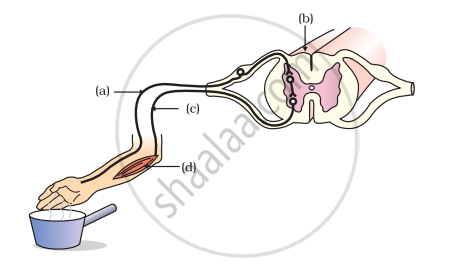
What are reflex actions? Give two examples. Explain a reflex arc.
From where the following nerves arise.
Auditory nerve
Which one is NOT a reflex action?
In the given diagram:
- Name the parts labelled A, B, and C.
- Write the functions of A and C.
- Reflex arcs have evolved in animals? Why?

Arrange and rewrite the terms in the group in the correct order to be in a logical sequence beginning with the term that is underlined:
Receptor, Response, Effector, Spinal Cord.
Arrange and rewrite the terms in group in the correct order to be in a logical sequence, beginning with the term that is underlined:
Effector, Receptor, Motor neuron, Sensory neuron.
