Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show with the help of a diagram, how a perfectly competitive firm earns a normal profit in short-run equilibrium.
Explain the short-run equilibrium of a perfectly competitive firm earning a supernormal profit with the help of a diagram.
उत्तर १
Under perfect competition, a firm’s average revenue curve is equal to the marginal revenue curve due to uniform prices for homogeneous goods. In, short-run, a competitive firm can earn supernormal profits, normal profits can also suffer losses. The adjacent diagram shows a perfectly competitive firm earning normal profits. Since the firm is a price taker, it has to decide the amount of output it should produce at the given price so as to maximise profits following the equilibrium conditions.
SMC = MR and AR = AC
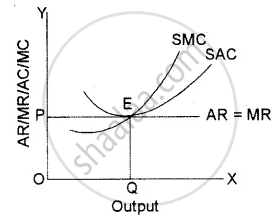
In the given diagram, OQ is equilibrium output, where SMC is equal to MR Since SAC is tangent to P = AR = MR line, the firm covers only its SAC, which includes normal profits.
उत्तर २
In the short term, a perfectly competitive firm can make a profit that is above average. This is when a company's total revenue exceeds its total costs. Firms are price takers in a completely competitive market, with the market price determined by the intersection of market supply and demand. When the market price exceeds the Average Total Cost (ATC) at the profit-maximising output level, a supernormal profit occurs. This scenario might be transient and is frequently the consequence of fortunate conditions such as increased product demand, technological advantages, or lower production costs than competitors. However, in the long run, the entry of new enterprises, drawn by the presence of above-average profits, increases the supply of the commodity, lowering the market price. The market price will eventually adjust to equal the average total cost and supernormal earnings will diminish, leaving just normal profits, which cover all costs.
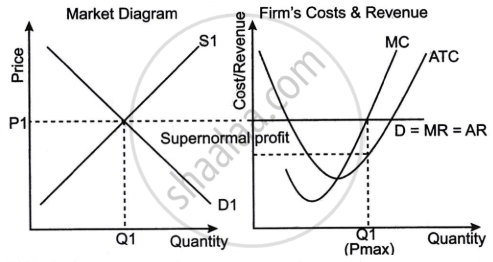
The diagram shows the firm's Marginal Cost (MC) curve intersecting the Average Total Cost (ATC) curve at a position lower than the Market Price (Pl), which is also equivalent to the firm's Marginal Revenue (MR). The difference between price and ATC at a quantity with MC = MR represents supernormal profit.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain ‘large number of buyers and sellers' features of a perfectly competitive market.
What is a price taker firm?
Explain the implications of the following : Perfect knowledge in perfect competition.
Explain Perfect knowledge about the markets feature of perfect competition.
Under what market condition does Average Revenue always equal Marginal Revenue? Explain.
Under which market form is a firm a price taker?
Why can a firm not earn abnormal profits under perfect competition in the long run? Explain.
Explain the implication of ‘freedom of entry and exit to the firms’ under perfect competition.
In which market form can a firm not influence the price of the product?
Explain how price is determined in a perfectly competitive market with fixed number of firms.
How is the optimal amount of labour determined in a perfectly competitive market?
Answer the following question.
Is a firm under perfect competition a price taker, or a price maker? Justify your answer.
Identify the market form and explain the corresponding feature, as given in the following statement:
"The commodity in this market has attributes which are identical for sellers and buyers."
Explain the short-run equilibrium of a firm facing losses under Perfect Competition.
A perfectly competitive firm always enjoys normal profit in the long run, irrespective of the situation it faces in the short run. Discuss the statement in brief.
