Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
When the centre of gravity is nearer to the base of a body, the body is in stable equilibrium.
Conditions for stable equilibrium:
(a) The body should have a broad base.
(b) Centre of gravity of the body should be as low as possible.
(c) Vertical line drawn from the centre of gravity should fall within the base of the support.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define equilibrium.
State the condition when a body is in dynamic equilibrium.
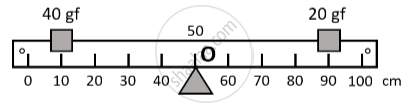
The figure shows a uniform metre rule placed on a fulcrum at its mid-point O and having a weight 40 gf at the 10 cm mark and a weight of 20 gf at the 90 cm mark.
- Is the metre rule in equilibrium? If not how will the rule turn?
- How can the rule be brought in equilibrium by using an additional weight of 40 gf?
A uniform meter scale is in equilibrium as shown in the diagram :
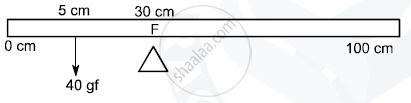
(i) Calculate the weight of the meter scale.
(ii) Which of the following options is correct to keep the ruler in equilibrium when 40 gf wt is shifted to 0 cm mark ?
F is shifted towards 0 cm
or
F is shifted towards 100 cm
State the principle of moments. A meter scale is pivoted at 30 cm mark and it is in equilibrium when a mass of 40 g is suspended from 10 cm mark. Calculate the mass of the ruler.
Give scientific reason for the following:
When a man climbs a slope he bends forward.
A faulty balance of unequal arms and pans of unequal weights is used to find the true weight of a metal. By double weighing the weights are found to be 1210 g and 1000 g. Calculate the true weight of the metal.
Explain why It is easier to knock down a boy who is standing on one foot than one who is standing on two.
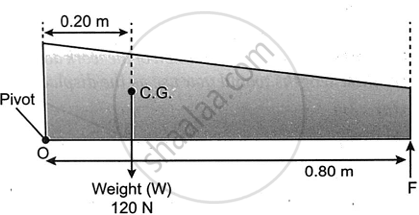
A non uniform beam of weight 120 N pivoted at one end is shown in the diagram below. Calculate the value of F to keep the beam in equilibrium.