Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
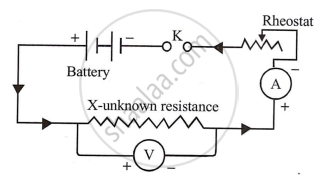
State Ohm’s law and draw a neat labelled circuit diagram containing a battery, a key, a voltmeter, an ammeter, a rheostat and an unknown resistance to verify it.
उत्तर
It states that electric current flowing through a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference V across its ends provided its temperature remains the same. This is called Ohm's law.
V = IR
Experimental Verification: Reassemble the circuit according to the diagram. The circuit consists of a battery, an unknown resistance, a voltmeter with its positive terminal facing the battery's anode, and a rheostat and ammeter connected in series. With the key closed, and the rheostat set to zero, the ammeter and voltmeter should display the lowest possible readings. After that, the rheostat is adjusted step-by-step, and the values of A and V are recorded at each interval. The ratio of `"V"/"I"` is always found to be constant. This verifies Ohm's Law.
The temperature and other physical parameters of the conductor must be kept constant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is an Ohmic resistor?
Write the formula of resistivity
The graph between V and I for a conductor is a straight line passing through the origin.
What should remain constant in a statement of this law?
Fill in the following blank with suitable words:
Resistance is measured in .............. The resistance of a wire increases as the length ..............; as the temperature ..............; and as the cross-sectional area .............. .
Calculate the current flowing through a wire of resistance 5 Ω connected to a battery of potential difference 3 V.
How does an increase in the temperature affect the specific resistance of a :
(i) Metal and
(ii) Semiconductor ?
Choose the correct alternative.
Which of the following is an ohmic conductor?
State Ohm’s law.
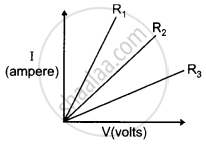
A student carries out an experiment and plots the V-I graph of three samples of nichrome wire with resistances R1, R2 and R3 respectively. Which of the following is hue?