Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
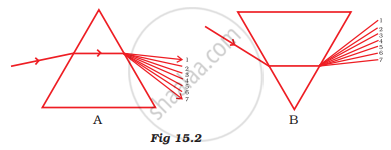
State the correct sequence (1-7) of colours in the spectrum formed by the prisms A and B, shown in Figure 15.2.
उत्तर
In figure A and figure B
| Figure A | Colour | Figure B |
| 1 | Red | 7 |
| 2 | Orange | 6 |
| 3 | Yellow | 5 |
| 4 | Green | 4 |
| 5 | Blue | 3 |
| 6 | Indigo | 2 |
| 7 | Violet | 1 |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A narrow beam PQ of white light is passing through a glass prism ABC as shown in the diagram.
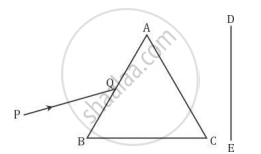
Trace it on your answer sheet and show the path of the emergent beam as observed on the screen DE.
(i) Write the name and cause of the phenomenon observed.
(ii) Where else in nature is this phenomenon observed?
(iii) Based on this observation, state the conclusion which can be drawn about the constituents of white light.
In the following ray diagram the correctly marked angle are:
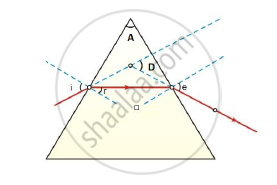
(a) ∠i and ∠e
(b) ∠A and ∠D
(c) ∠i, ∠e and ∠D
(d) ∠r, ∠A and ∠D
State the cause of dispersion of white light
What do you understand by the term spectrum? Name the various colours present in the spectrum of sunlight.
- A beam of monochromatic light undergoes minimum deviation through an equiangular prism, how does the beam pass through the prism, with respect to its base?
- If white light is used in the same way as in part (a) above, what change do you expect in the emergent beam?
- What conclusion do you draw about the nature of white light in part (b)?
Complete the ray diagram given below to show the nature of light produced on the screen.

Draw a labeled ray diagram to illustrate the dispersion of a narrow beam of white light when it passes through a glass prism.
Sunlight entering through a narrow aperture falls on a prism. Draw a neat labelled ray diagram to show the formation of the spectrum on a screen. Name the colour obtained nearer the base of the prism.
Match the Columns:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| The wavelength of red light | (a) 600 nm |
| (b) 700 nm | |
| (c) 500 nm |
